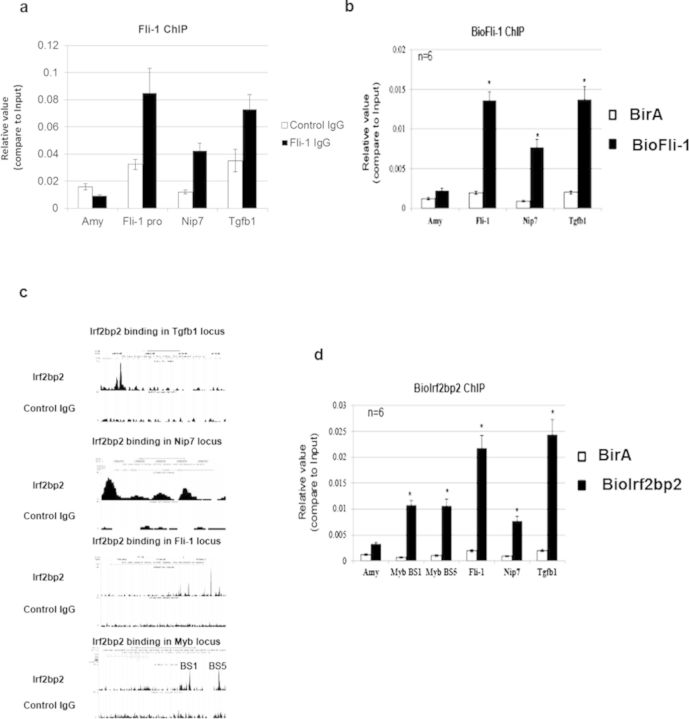
Figure 4.
NLS-tagged Fli-1 and Irf2bp2 are recruited to the endogenous protein target regions. (a) ChIP experiments with the anti-Fli-1 antibody (black bars) or the Control IgG (white bars) from MEL cells followed by qPCR using primers amplifying β-amylase (control region), Fli-1 promoter, Nip7 promoter and a region within the Tgfb1 locus. Data represents the average of three independent experiments; error bars denote standard deviation. (b) Streptavidin-ChIP from MEL/BirA (white bars) and MEL/BioFli-1 (black bars) cells followed by qPCR using primers amplifying β-amylase (control region), Fli-1 promoter, Nip7 promoter and a region within the Tgfb1 locus. Data represents the average of six independent experiments; error bars denote standard deviation, *P < 0.05, Student's t-test between MEL/BirA and MEL/BioFli-1 cells. (c) Genome-wide Irf2bp2 binding sites in MEL cells were identified by ChIP-Seq experiments. The different Irf2bp2 genomic binding regions can be visualized by the UCSC genome browser. For example, Irf2bp2 binds a region within the tgfb1 locus, the nip7 gene promoter, the fli-1 gene promoter and two known enhancers of c-myb gene (BS1: Myb −36 kb; BS5: Myb −68 kb). (d) Streptavidin-ChIP from MEL/BirA (white bars) and MEL/BioIrf2bp2 (black bars) cells followed by qPCR using primers amplifying β-amylase (control region), Myb −36 kb (BS1), Myb −68 kb (BS5), Fli-1 promoter, Nip7 promoter and a region within the Tgfb1 locus. Data represents the average of the signal for six independent experiments; error bars denote standard deviation, *P < 0.05, Student's t-test between MEL/BirA and MEL/BioIrf2bp2.