Figure 2.
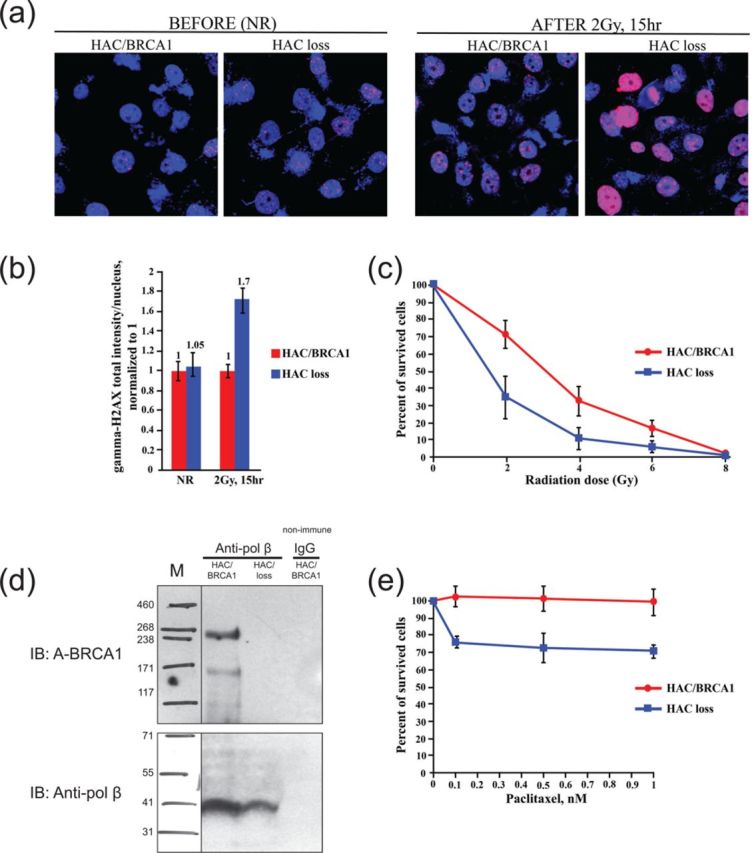
Complementation tests for functionality of BRCA1 in UWB1.289 cells. (a) Accumulation of γ-H2AX in BRCA1-deficient cells (UWB1.289) carrying alphoidtetO-HAC/BRCA1 and in the cells that have lost the HAC after exposure to 2 Gy of γ-rays. Cells were stained 15 h after irradiation with anti-γ-H2AX antibodies (red) and with DAPI (blue). Representative microscopic fluorescence images of γ-H2AX foci accumulation are shown. (b) Quantitative data for γ-H2AX foci processing. Cells were collected after 15 h and the average number of γ-H2AX foci was quantified in BRCA1-positive and BRCA1-negative cells. NR cells have been included as a control. (c) Radiation sensitivity clonogenic survival assay. BRCA1-deficient UWB1.289 cells are radiation sensitive. Cells carrying alphoidtetO-HAC/BRCA1 and after HAC loss were plated in triplicate and irradiated with the indicated doses (from 0 to 8 Gy). Cells were stained with crystal violet and counted visually. Clonogenic survival was calculated as a number of colonies present in each plate normalized to the number of colonies in the NR control plates. Cells carrying alphoidtetO-HAC/BRCA1 (red) are less sensitive than the cells that lost the HAC (blue). Bars, mean of triplicate samples. (d) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis of BRCA1 and pol β proteins interaction. Cell extracts from the cells carrying alphoidtetO-HAC/BRCA1 and from the cells that have lost the HAC were immunoprecipitated with anti-pol β antibody or non-immune IgG. Immunoprecipitated proteins were detected by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. (e) Viability of UWB1.289 cells carrying alphoidtetO-HAC/BRCA1 (red) and after HAC loss (blue) after treatment with paclitaxel. At 24 h after treatment the cell viability was measured. All experiments were repeated three times with each sample prepared in triplicate.
