Figure 3.
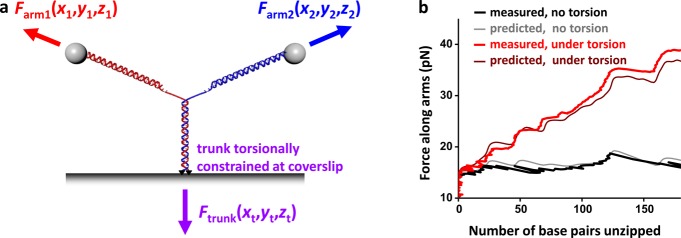
Unzipping a Y structure under torsion. (a) The trunk of the Y structure was torsionally constrained to the microscope coverslip via multiple fluorescein/antifluorescein connections at both DNA strands of the trunk end. This Y structure version prevented the trunk end from swiveling around the anchoring points. (b) Force along arms versus number of base pairs unzipped of either a torsionally constrained or unconstrained trunk, both under 8 pN trunk force. Theoretical predictions are shown for comparison. Data were taken at 10 kHz and filtered to 20 Hz.
