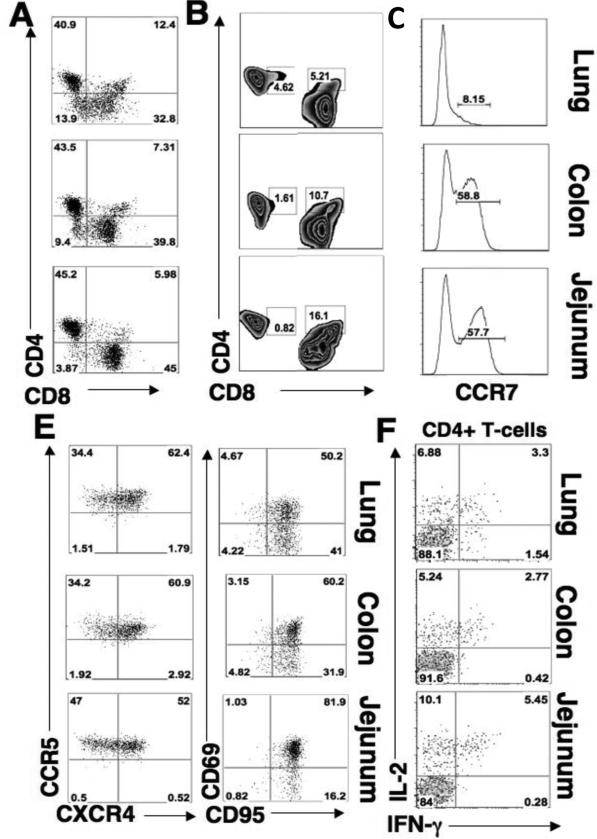
Figure 1. Lung and gastrointestinal mucosal sites have comparable levels of activated memory CD4+ T-cells.
Flow cytometry was performed to determine the percentages of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells in uninfected mucosal tissues with respect to lymphocyte subtypes. (A) Percentage of CD4+ versus CD8+ in lung (upper), colon (middle), and jejunum (lower). (B) Percentage of CD4+ T-cells that co-express CD8 (CD4+highCD8+low) and the percentage of CD8+ T-cells that express CD4+ (CD8+highCD4+low) in mucosa. (C) Percentage of central memory (CCR7+) CD4+ T-cells in lung, colon, and jejunum. (D) Percentage of CD4+ T-cells that express CCR5 or CXCR4 in lung, colon, and jejunum. (E) Percentage of CD4+ T-cells that express CD95 versus CD69 in lung, colon, and jejunum. (F) Percentage of CD4+ T-cells cells that secrete IL-2 or IFN-γ upon SEB stimulation.