FIGURE 1.
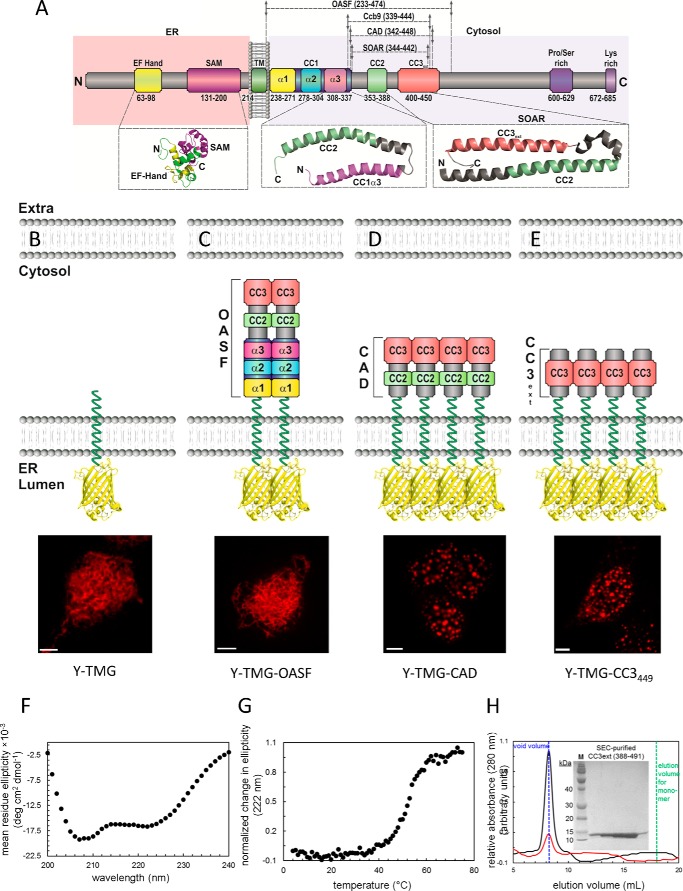
Coiled-coil 1 controls formation of CAD clusters. A, scheme of STIM1 depicting individual domains: ER luminal EF hand and SAM domain, transmembrane domain (TM), coiled-coil (CC) domains: CC1 subdivided into α1, α2, α3, respectively, CC2, CC3, Pro/Ser-rich domain, Lys-rich domain. Numbers correspond to amino acid positions of human STIM1. Below, solution NMR structures of STIM1 N-terminal domains as well as of the CC1α3-CC2 fragment, and the crystal structure of SOAR are magnified. B–E, FIRE system: schemes of FIRE constructs (Y-TMG-x; x: OASF, CAD, CC3449) used for fluorescence imaging experiments. Y (YFP) is located in the ER lumen, STIM1 fragments are located on the cytosolic side, attached via a Gly-linker to the ER transmembrane segment. All constructs were overexpressed in HEK 293 cells, and representative images are depicted: (B) Y-TMG (control) showed ER distribution without cluster formation. (C) Y-TMG-OASF resulted in ER distribution and no cluster formation. Y-TMG-CAD (D) and Y-TMG-CC3449 (E) revealed clear cluster formation. The bar in each fluorescence image corresponds to 5 μm. F, far-UV-CD spectrum of STIM1 CC3ext. The negative ellipticity minima at 208 and 222 nm are indicative of an α-helical fold. The spectrum was acquired at 0.25 mg ml−1 and is an average of 3 scans. G, thermal stability of STIM1 CC3ext. The sigmoidal unfolding profile suggests a cooperative unfolding and is consistent with the high α-helicity of CC3ext. The thermal melt was acquired at 0.25 mg ml−1. H, SEC of STIM1 CC3ext. After 100-μl injections of 1.25 mg ml−1 (black trace) and 0.25 mg ml−1 (red trace), CC3ext eluted in the void volume of the Superdex 200 10/30 GL column (blue vertical broken line) indicative of higher order oligomers with a molecular mass > 600 kDa. The expected elution volume of monomeric CC3ext is shown for reference (green vertical broken line). Inset depicts a Coomassie Blue-stained SDS-Page gel for fractions recovered following gel filtration showing monomeric CC3ext of 12.2 kDa.