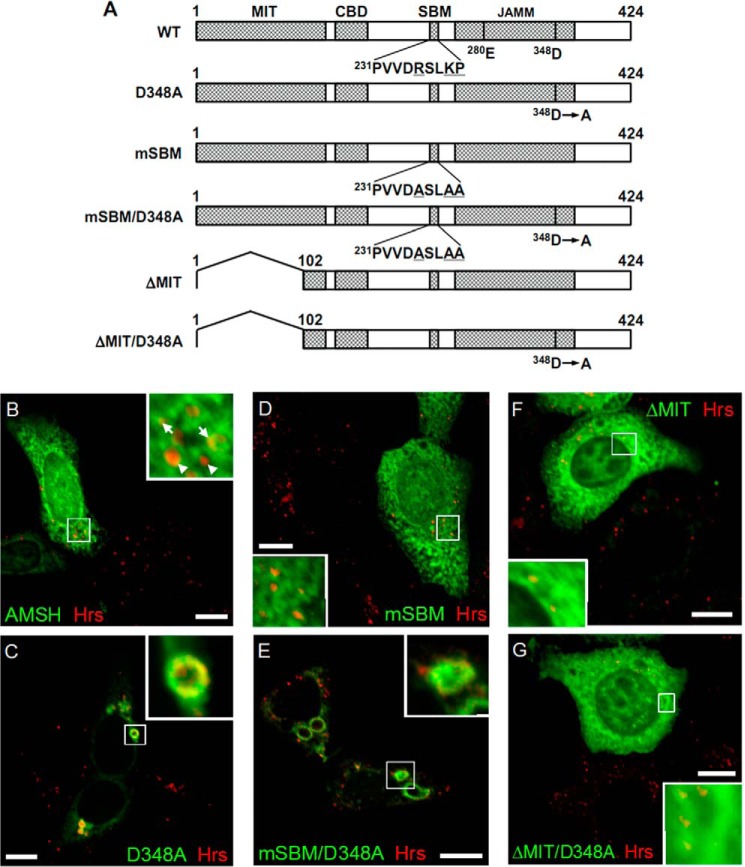
FIGURE 8.
STAM-mediated endosomal dissociation of Hrs is independent of STAM-associated deubiquitylating activity. A, schematic representation of the structure of the AMSH deletion mutants. The microtubule interacting and transport (MIT) domain, clathrin-binding domain (CBD), STAM-binding motif (SBM), and JAB1/MPN/Mov34 metalloprotease (JAMM) domains are indicated at the top of the diagram. The putative catalytic (Glu280) and metal-binding (Asp348) residues in the active site are indicated. The mutated residues in the SBM are underlined. B–G, HEK293T cells were transfected with wild-type AMSH, AMSH-D348A, AMSH-mSBM, AMSH-mSBM/D348A, AMSH-ΔMIT, or AMSH-ΔMIT/D348A and were then immunostained for endogenous Hrs and AMSH or the AMSH mutants. B, AMSH partially co-localizes with endogenous Hrs but does not induce morphological changes in Hrs-positive endosomes. Arrows in the inset indicate Hrs-positive endosomes co-localizing with AMSH, and arrowheads indicate Hrs-positive but AMSH-negative endosomes. C, deubiquitylating activity-deficient AMSH (AMSH-D348A) induces endosomal swelling. D, STAM1-binding-deficient AMSH (AMSH-mSBM) does not co-localize with Hrs. E, expression of the AMSH mSBM and the D348A double mutant (AMSH-mSBM/D348A) leads to the enlargement of Hrs-positive endosomes. F and G, both ESCRT-III binding-deficient AMSH (AMSH-ΔMIT) and ΔMIT and the D348A double mutant (AMSH-ΔMIT/D348A) co-localize with endogenous Hrs but have no effect on endosomal morphology. Scale bars, 10 μm.