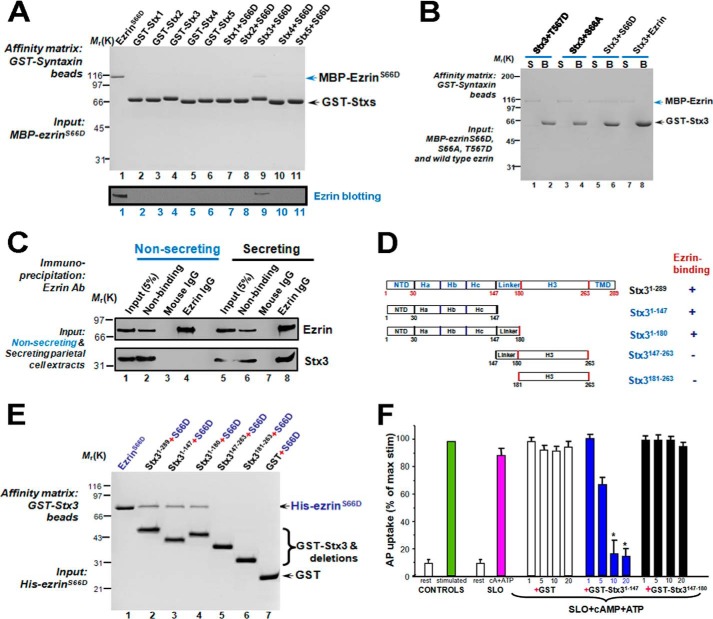
FIGURE 2.
Phosphorylation of Ser-66 on ezrin is essential for ezrin-Stx3 interaction and parietal cell acid secretion. A, phosphorylation of Ser-66 of ezrin specifies its association with Stx3. Various GST-syntaxin proteins were purified on glutathione-Sepharose beads followed by incubation with MBP-ezrinS66D. Beads were washed and boiled in SDS-PAGE sample buffer followed by SDS-PAGE analyses of proteins bound to the beads. Western blotting analyses shown on the bottom panel confirmed that Stx3 selectively binds to EzrinS66D. B, Stx3 specifically binds to ezrinS66D but not ezrinS66A, ezrinS567D, or wild type ezrin. GST-Stx3 proteins were purified on glutathione-Sepharose beads followed by incubation with MBP-ezrinS66D, MBP-ezrinS66A, MBP-ezrinS567D, or wild type ezrin proteins. Beads were washed and boiled in SDS-PAGE sample buffer followed by SDS-PAGE analyses of proteins bound to the beads. R, resting; S, stimulated. C, Stx3 forms a cognate complex with ezrin. Ezrin immunoprecipitation pulled down Stx3 from secreting parietal cells. D, diagram of Stx3 deletion mutants. NTD, N-terminal domain; TMD, terminal transmembrane domain. E, mapping the domains of Stx3 responsible for ezrinS66D binding. Note the Habc domain of Stx3 binds to ezrinS66D. F, Habc domain of Stx3 inhibits acid secretion in SLO-permeabilized gastric glands. Glands were SLO-permeabilized and incubated with various Stx3 deletion mutants before being stimulated with 100 μm cAMP plus 100 μm ATP, and the AP uptake was measured as described under “Materials and Methods.” AP data are plotted as a percentage of the stimulated control for each experiment. Error bars represent S.E.; n = 5. *, significant difference from stimulated controls (p < 0.001).