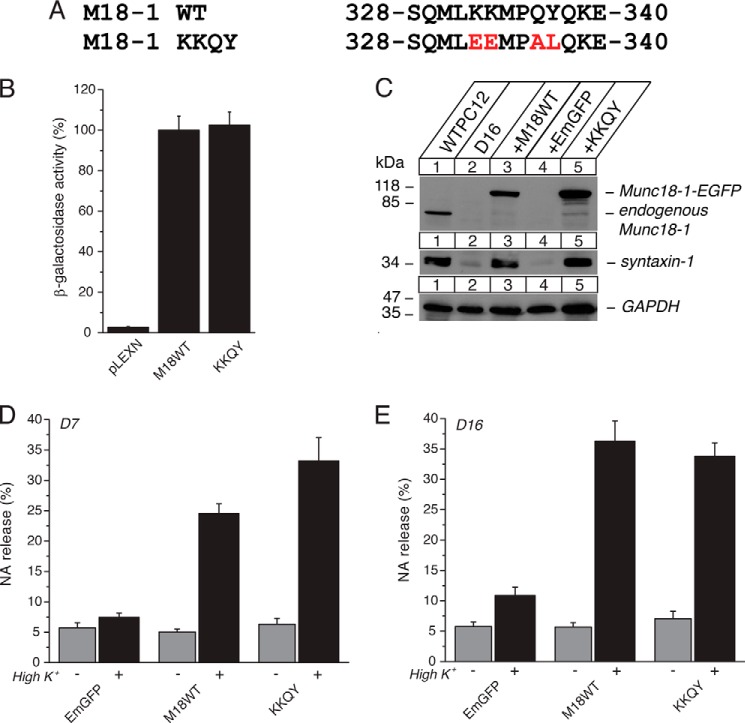
FIGURE 4.
The quadruple K332E/K333E/Q336A/Y337A (KKQY) mutant retains the ability of Munc18-1 to interact with syntaxin-1, to restore syntaxin-1, and to restore secretion. A, sequence alignment of the KKQY mutant containing mutations at Lys-332, Lys-333, Gln-336, and Tyr-337. Mutated residues are shown in red. M18-1, Munc18-1. B, the binding between Munc18-1 domain-3a KKQY mutant and syntaxin-1 or Mint-1 was analyzed by yeast two-hybrid assays. In this assay, β-galactosidase activities of the transformed yeast clones were quantified and normalized so that the activity of the yeast clones transformed with the wild-type Munc18-1 was set to 100%. Error bars indicate S.E. (n = 16 for syntaxin-1 interaction; n = 10–12). C, stable re-expression of Munc18-1 KKQY mutant in D7 or D16 clone restores syntaxin-1 levels. EGFP, emerald green fluorescent protein. D, secretion defects are rescued upon reintroduction of the KKQY-EmGFP mutant in Munc18-1/-2 double knockdown cells (D7 clone). NA release was stimulated by 70 mm KCl for 15 min in the rescued cells. Error bars indicate S.E. (n = 7–13). E, secretion defects not rescued upon reintroduction of the KKQY-EmGFP mutant in Munc18-1/-2 double knockdown cells (D16 clone). NA release was stimulated by 70 mm KCl for 15 min in the rescued cells. Error bars indicate S.E. (n = 9–12).