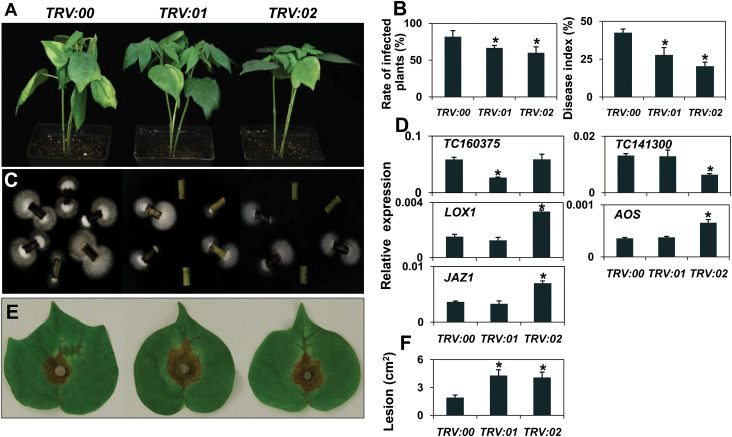
Fig. 4.
TC160375- and TC141300-VIGS cotton plants show enhanced Verticillium resistance but were more susceptible to B. cinerea. (A) Ten-day-old cotton plants were agroinfiltrated with recombinant TRV vector carrying a fragment of TC160375 or TC141300. TRV empty vector was also agroinfiltrated into plants as the vector control. Two weeks later, these plants were inoculated with V. dahliae. Photographs were taken 8 days after V. dahliae inoculation. (B) The proportion of infected plants and disease index of VIGS-silenced plants 10 days post-inoculation by V. dahliae. (C) For the fungal recovery assay, the stem sections taken from cotton seedlings 10 days after V. dahliae inoculation were incubated at 25 °C on potato dextrose agar, photographed 4 days after inoculation. (D) Transcript levels of TC160375, TC141300 and several JA-dependent genes were determined by qPCR. TC160375 and TC141300 transcripts were detected in root tissue of VIGS plants. UBQ7 was used as an internal control. (E) Leaves of VIGS seedlings were inoculated with B. cinerea in vitro, and photographed after 3 days. (F) Size of lesions induced by B. cinerea was measured after 3 days of inoculation. TRV:00, TRV:01 and TRV:02 refer to vector controls, TC160375- and TC141300-VIGS plants, respectively. Similar results were obtained with three replicates. Each column represents an average of three biological repeats. * Indicates significant differences relative to the vector control at P < 0.05. A colour version of this figure is available at JXB online.