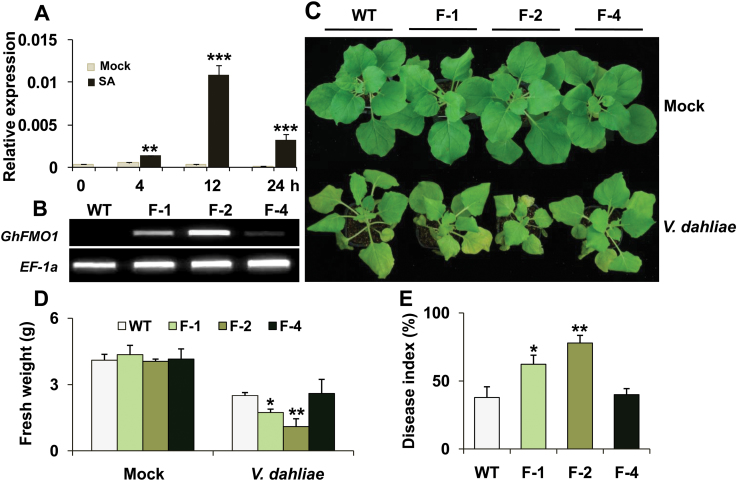
Fig. 5.
GhFMO1 was dramatically upregulated following SA treatment in cotton and enhanced susceptibility to V. dahliae in tobacco. (A) Two-week-old cotton seedlings were mock-treated (control) or treated with 10mM SA. Expression of GhFMO1 in root tissues under control conditions and SA treatment at the indicated time points was analysed by qPCR. (B) Expression analysis of GhFMO1 in WT and transgenic tobacco lines (F-1, F-2 and F-4) by RT-PCR. NbEF-1α was used as an internal control in tobacco. (C) Four-week-old WT and transgenic tobacco plants were mock inoculated or inoculated with V. dahliae, and photographed at 14 days post-inoculation. (D, E) The weight and disease index of WT and transgenic tobacco plants were measured 14 days after V. dahliae infection. Each column represents the average of three independent replicates. *, ** and *** indicate significant differences relative to the control at P < 0.05, P < 0.01 and P < 0.001, respectively. A colour version of this figure is available at JXB online.