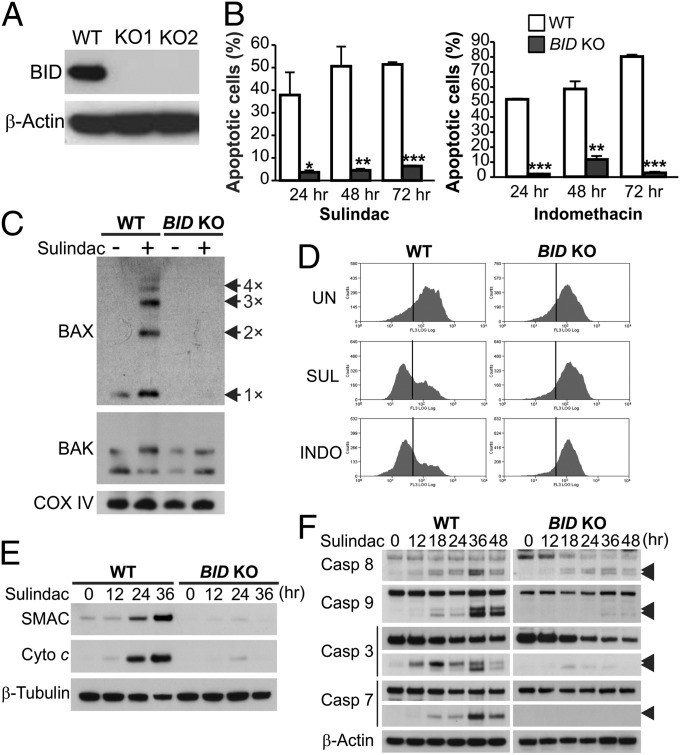
Fig. 4.
BID mediates NSAID-induced apoptosis in CRC cells through the mitochondrial pathway. (A) Western blot of BID in WT and two independent clones of BID knockout (BID KO) HCT116 cell lines. (B) Apoptosis at indicated time points in WT and BID KO HCT116 cells treated with 120 µM sulindac sulfide or 500 µM indomethacin was analyzed by counting cells with condensed and fragmented nuclei. Results were expressed as means + SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (C) BAX and BAK multimerization was analyzed by cross-linking the mitochondrial fractions isolated from cells treated as in B for 36 h, followed by SDS/PAGE under nonreducing conditions and Western blotting. Cox IV, a mitochondrial protein, was used as a control for loading and fractionation. (D) Mitochondrial membrane potential in cells untreated (UN) or treated with sulindac sulfide (SUL) or indomethacin (INDO) as in B for 48 h was analyzed by MitoTracker Red staining followed by flow cytometry. (E) Cytochrome c (Cyto c) and SMAC/DIABLO release were analyzed by Western blotting of cytosolic fractions isolated from cells treated with sulindac sulfide as in C. α-Tubulin, a cytosolic protein, was used as control for loading and fractionation. (F) Western blot of caspase (Casp) activation at the indicated time points in cells treated as in B. Arrowheads indicate caspase cleavage fragments.