Fig. 1.
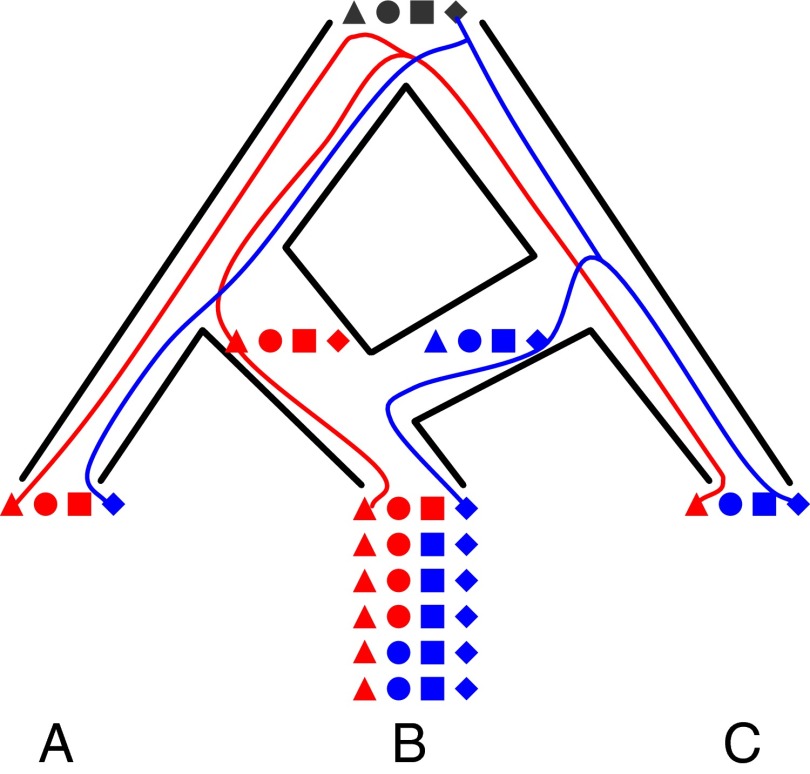
Phylogenetic networks. Here, the MRCA of A and B split from its MRCA with C, and some time after A and B split, hybridization occurred between B and C. Four independent loci, ▲, ●, ■, and ♦, are illustrated, for which a single individual is sampled from each of A and C and six individuals are sampled from B. Two gene trees are depicted for the ▲ and ♦ loci, and both trees agree in terms of their shapes. However, the disagreement of the species splitting pattern with the gene tree in red is due to ILS, whereas the disagreement with the gene tree in blue is due to hybridization. Furthermore, the ▲ locus exhibits no evidence of hybridization in B, the ♦ locus has lost all signal of vertical inheritance from the MRCA of B with A, and the other two loci exhibit varying degrees of hybridization signal in the population. Locus-specific inheritance probabilities are needed to capture such scenarios.