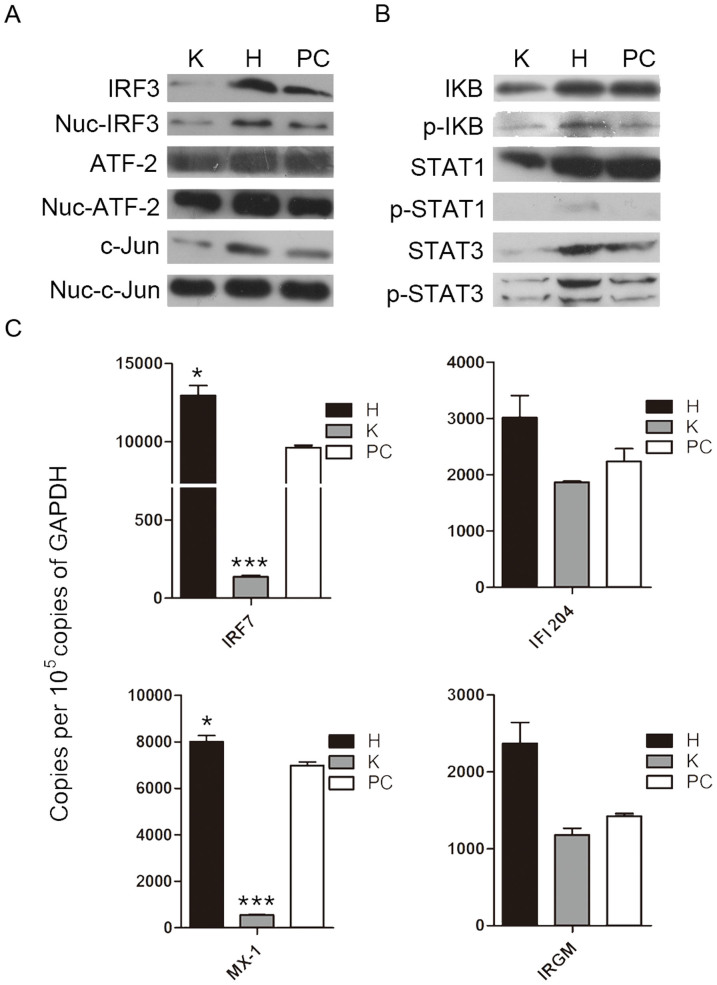
Figure 2. Interferon signaling pathways participate in hesperidin- and kaempferol-induced opposite antiviral state.
A549 cells were infected with Influenza A/WSN/33 virus for 3 h, and then treated with hesperidin or kaempferol for 24 h, 0.05% DMSO as a control (PC). The proteins related to interferon signaling pathways were detected by western blot. The total and the nuclear proteins of activating transcription factor 2 (ATF-2), JUN gene coded protein (C-jun) and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) (A). Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (IκB), signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 (STAT1) and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3) proteins and their phosphorylation levels (B), GAPDH gene expression level is a control as in Fig. 1C. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 15. Interferon-induced expression of antiviral genes, including: interferon-induced GTPase (MX-1), immunity-related GTPase family M protein (IRGM), interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) and interferon activated gene 204 (IFI204) was analyzed by Q-PCR (c), data were presented as means ± SEM of three independent experiments, * p < 0.05; **p < 0.01;***p < 0.001, compared with untreated cells, mRNA expression of each target gene was normalized to GAPDH mRNA expression. H represented hesperidin; K represented kaempferol.