Figure 3.
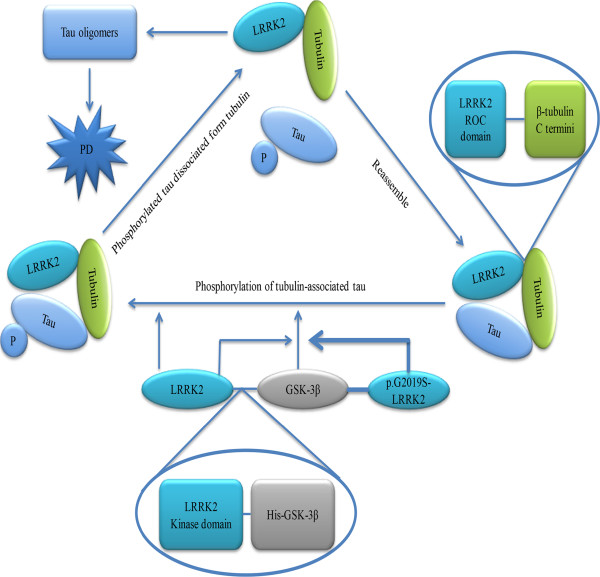
The possible pathogenic mechanism links LRRK2 and Parkinson’s disease α-synuclein, tau, inflammatory response, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, synaptic dysfunction and autophagy-lysosomal system all take part in the pathogenic of PD. Open and filled arrows show positive (activating) and negative (suppressing) interactions, respectively.
