Figure 1.
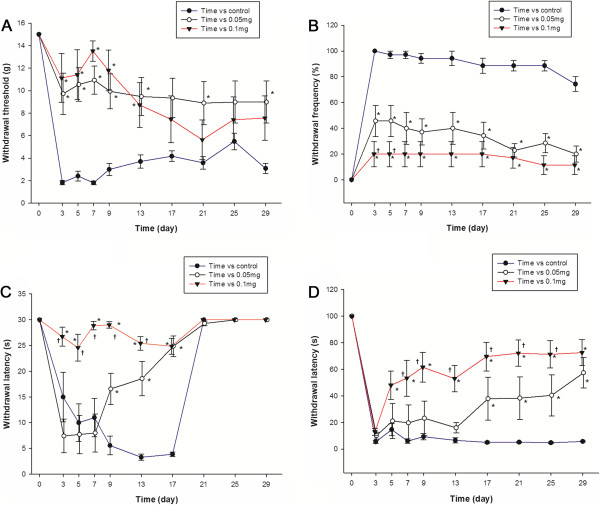
The results of behavioral testing after perineural diluted bee venom (DBV) pretreatment in time–course. A. Mechanical allodynia was suppressed in rats pretreated with diluted bee venom (DBV), relative to the control group. The paw withdrawal threshold in both DBV treated groups were significantly higher compared with the control group from observation day 3 to day 13. B. DBV effect on acetone stimulation test in rats. Cold allodynia was inhibited, beginning on day 3 in both groups of rats treated with DBV, compared with the control group and continued until the end of study. C. DBV effect on hot plate test in rats. Thermal allodynia was inhibited from day 3 until day 17 in 0.1 mg DBV group, and day 9 to day 17 in 0.05 mg DBV group. The PWL of control and both BV treated groups restored to normal values beginning on day 21. The preservation of PWL was dose related, being significantly higher in rats treated with 0.1 mg than with 0.05 mg DBV on days 3, 5, 7, 9, and 13. D. DBV effect on cold plate test in rats. The development of cold allodynia after SNL was inhibited in the rats pretreated with DBV, especially in the 0.1 mg group, beginning on day 5 until the end of study. The 0.1 mg DBV group presented significantly longer PWL compared with 0.05 mg group throughout the study period. Each point represents mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). *p < 0.05 compared with the control group. †p < 0.05 compared with the BV 0.05 mg group. n = 7 animal per group.
