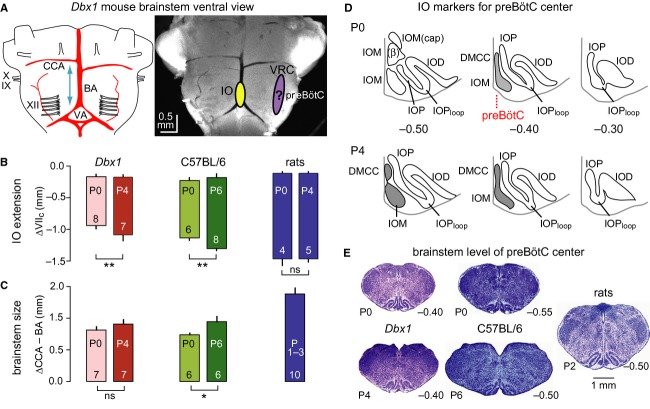
Figure 2.
Comparative analyses of positions of inferior olive (IO), brainstem dimension, and preBötC location in Dbx1 reporter mice, C57BL/6 mice, and Wistar/Sprague–Dawley rats. (A) Ventral brainstem of a postnatal day 4 (P4) Dbx1ERCreT2; Rosa26tdTomato mouse. BA, basilar artery; CCA, caudal cerebellar artery; IO, inferior olive; IX, glossopharyngus nerve; preBötC, pre‐Bötzinger complex; VA, vertebral artery; VRC, ventral respiratory column; X, vagus nerve; XII, hypoglossal nerve. The approximate positions of the medial IO (IOM) and preBötC within the rostrocaudal ventral respiratory column are projected onto the brainstem photograph. (B) IO extension referred to the distance from the caudal end of facial motor (VII) nucleus, VIIc. Vertical bars show mean (±SD) of the rostral and caudal borders of the IO for each strain and species, as well as age. Asterisk and double asterisks indicate statistical significance at P <0.05 and P <0.01, respectively. Numerals indicate brainstems analyzed. (C) Brainstem dimension quantified as the distance from the mean value of the left and right CCA to the point at which the BA bifurcates to form the VAs. (D) Subgroups of the IO in transverse sections of P0 and P4 Dbx1 reporter mouse brainstems, which mark the location of the preBötC center (see red dotted line). Other abbreviations: IOD, dorsal IO; IOP, principal IO; IOPloop, lateral loop of IOP; DMCC, dorsomedial cell column of IO; IOM (ß), ß subgroup of IOM; IOM (cap), dorsal cap subgroup of IOM. We hypothesize that the preBötC center colocates with the level where the DMCC joins with the medial aspect of the IOM to form a vertical stalk. (E) Characteristic histological (thionin‐stained) brainstem sections at the presumed center of the preBötC. Calibration bar on right applies to all images. Data from C57BL/6 mice and newborn Wistar/Sprague–Dawley rats in (B) and thionin‐stained sections in (E) are taken from our previous studies Ruangkittisakul et al. (2006, 2011), respectively.