Fig. 1.
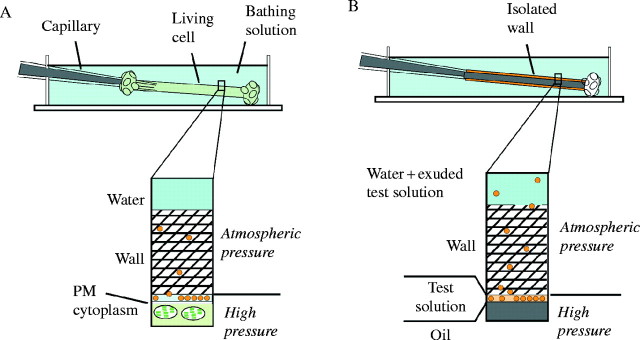
Measuring and altering P inside (A) a living Chara corallina internode cell or (B) an isolated wall when a test solution of polymers is present at the inner wall face. Molecules recently released from the plasma membrane (A) or molecules from the test solution (B) are shown (yellow). The matrix of the wall is the cross-hatched region and contains embedded cellulose microfibrils that are not shown. The pressure probe capillary in (A) removes or returns cell solution to the cell interior allowing control of P. The pressure probe capillary in (B) removes or returns mineral oil to the wall lumen allowing control of artificial P. The oil/water meniscus in (B) is at the same position as the plasma membrane (PM) in (A). Wall interstices remain filled with water and at atmospheric pressure.
