Fig. 4.
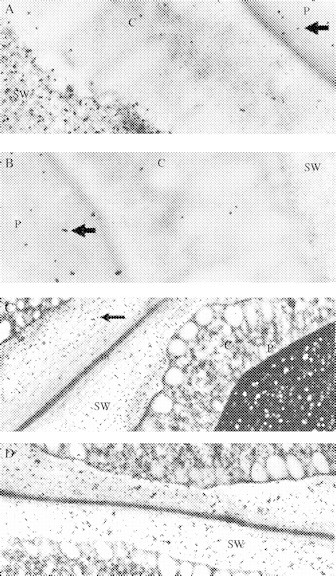
Cytochemical controls using sections of 16-h imbibed lupin cotyledons. (A) Enzyme boiled (5 min) before gold complexing (×32 000); (B) addition of lupin (1→4)-β-galactan during staining with the gold-complexed enzyme (×32 000). (C) Enzyme boiled (5 min) before gold complexing (×13 300); (D) Pre-incubated with active exo-(164)-β-galactanase before staining with heat-deactivated gold complex (×13 300). After in vitro hydrolysis with exo-galactanase clusters with higher density can be seen, but no gold particles stained them. We assumed that these clusters are probably due to the appearance of the fibrous material that is left after hydrolysis, as shown in Figure 7B. Arrows in (A), (B) and (C) point to gold particles. c, cytoplasm; P, protein body; SW, storage wall.
