FIGURE 1.
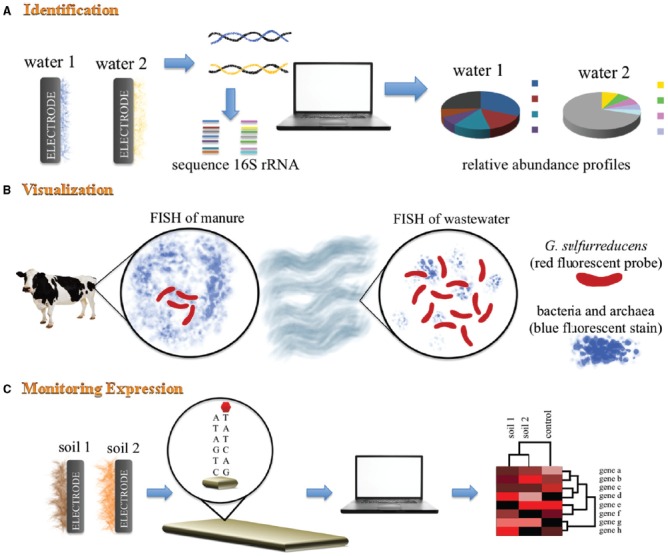
Schematic representation of mixed BES community analyses. (A) 16S rRNA gene sequencing analysis is used to identify dominant microorganisms found in electrode-associated communities. This fingerprinting technique provides an overview of the phylogenetic diversity within the electrode-associated communities. (B) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) using DAPi blue fluorescent stain for bacteria and archaea, and a species-specific probe for G. sulfurreducens. This technique allows identification, visualization and quantification of G. sulfurreducens within mixed BES communities from different environmental niches. (C) Geochip analysis of different metagenomic samples allows for specific genes of known function to be probed and identified.
