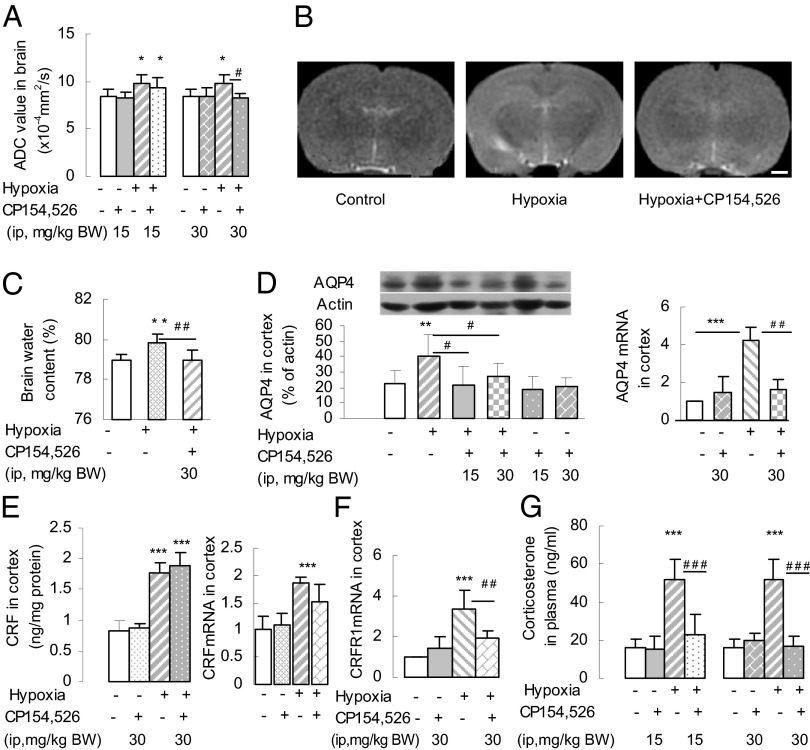
Fig. 1.
Simulated high-altitude hypoxia induced brain edema in rats. (A) Increases in ADC values determined by MRI after hypoxia were abolished by pretreatment with the CRFR1 antagonist CP154,526 (30 mg/kg) (n = 6 or 7 per group). *P < 0.05 (vs. control); #P < 0.05 (vs. hypoxia). (B) Representative MRI images of rat brain: control, hypoxia, and pretreatment with CP154,526 + hypoxia (hypoxia+CP154,526). (Scale bar: 1 mm.) (C) Elevation of brain water content after hypoxia was blocked by CP154,526 (n = 6 or 7). **P < 0.01 (vs. control); ##P < 0.01 (vs. hypoxia). (D) Hypoxia increased the expression of AQP4 and AQP4 mRNA in the cortex, and the increase of AQP4 protein and AQP4 mRNA was blocked by CP154,526 (n = 6 or 7). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 (vs. control); #P < 0.05; ## P < 0.01 (hypoxia vs. antagonist + hypoxia). (E) Hypoxia-induced increases in CRF content and CRF mRNA expression in cortex were not abolished by CP154,526 (n = 6 or 7). ***P < 0.001 (vs. control). (F) CRFR1 mRNA expression in the cortex was increased by hypoxia, and this increase was abolished by CP154,526 (n = 6 or 7). ***P < 0.001 (vs. control); ##P < 0.01 (vs. hypoxia). (G) Hypoxia increased the plasma concentration of corticosterone and this effect was abolished by CP154,526 (n = 6 or 7). ***P < 0.001 (vs. control); ###P < 0.001 (vs. hypoxia).