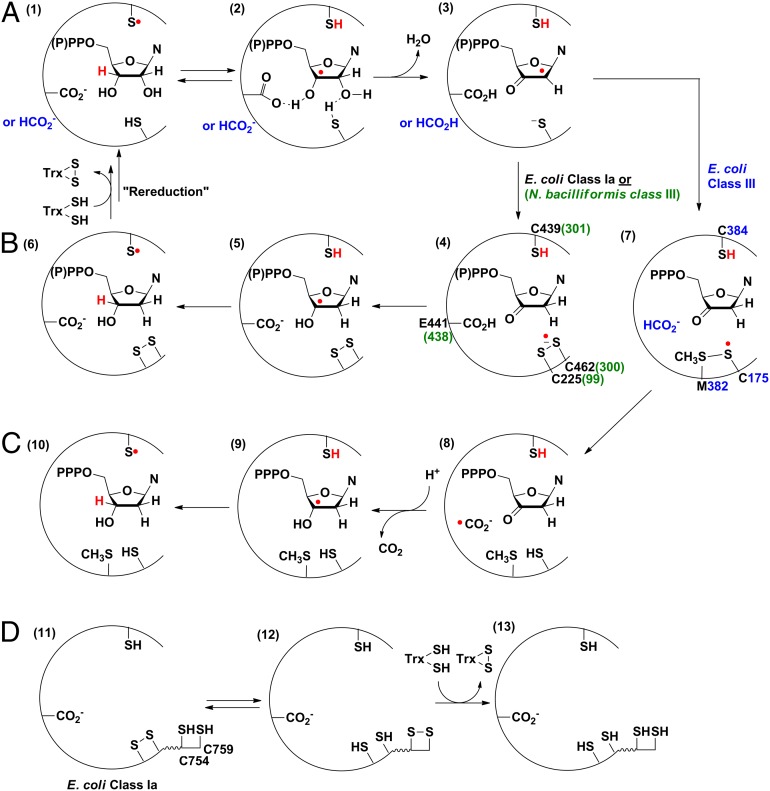
Fig. 1.
Mechanistic model for nucleotide reduction by RNRs. (A) First half reaction common to all RNRs. (B) Second half reaction of E. coli class Ia and N. bacilliformis class III RNR. (C) Second half reaction of E. coli class III RNR. M382 in E. coli class III RNR is located two residues from the top face thiyl radical (C384), in a position similar to the conserved N437 in E. coli class Ia RNR, which makes a hydrogen bond to the 2’-OH group of the substrate. (D) Mechanistic model for rereduction of the active site disulfide in class I and II RNRs via a pair of conserved cysteines on the C-terminal tail of α.