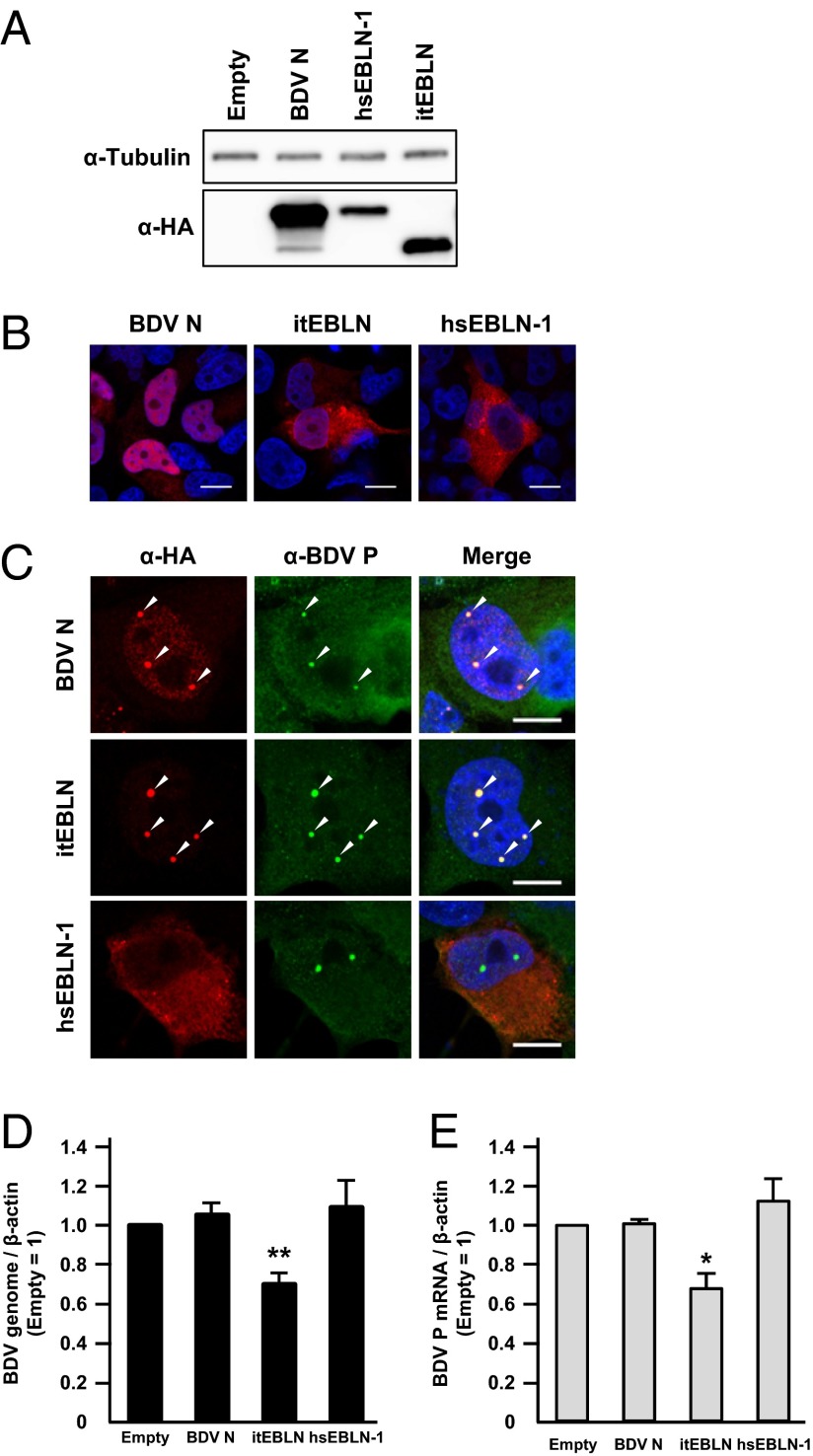
Fig. 1.
Expression of itEBLN inhibits BDV replication in transfected human cells. (A) Expression of recombinant EBLN proteins in transiently transfected OL cells. The HA-fused itEBLN, hsEBLN-1, and BDV N constructs were transfected into OL cells, and the expressed proteins were detected by Western blotting using anti-HA antibody. (B and C) Subcellular localization of recombinant EBLNs in transfected cells. The expression plasmids were transfected into uninfected cells (B) and OL cells persistently infected with BDV (C), and the distributions of EBLN proteins and BDV P were visualized by immunofluorescence assay with anti-HA (red) and anti-P (green) antibodies, respectively. Cells were counterstained with DAPI. Arrowheads in C indicate vSPOTs (bornavirus viral factories). (Scale bars, 10 μm.) (D and E) Expression of itEBLN decreases the level of BDV RNAs in persistently infected cells. Forty-eight hours after transfection of the indicated constructs, the amounts of BDV genomic RNA (D) and mRNA (E) were quantified by real-time RT-PCR. The bars labeled “Empty” represent cells transfected with an empty vector. The values are presented as the mean ± SE of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was analyzed by the two-tailed t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.