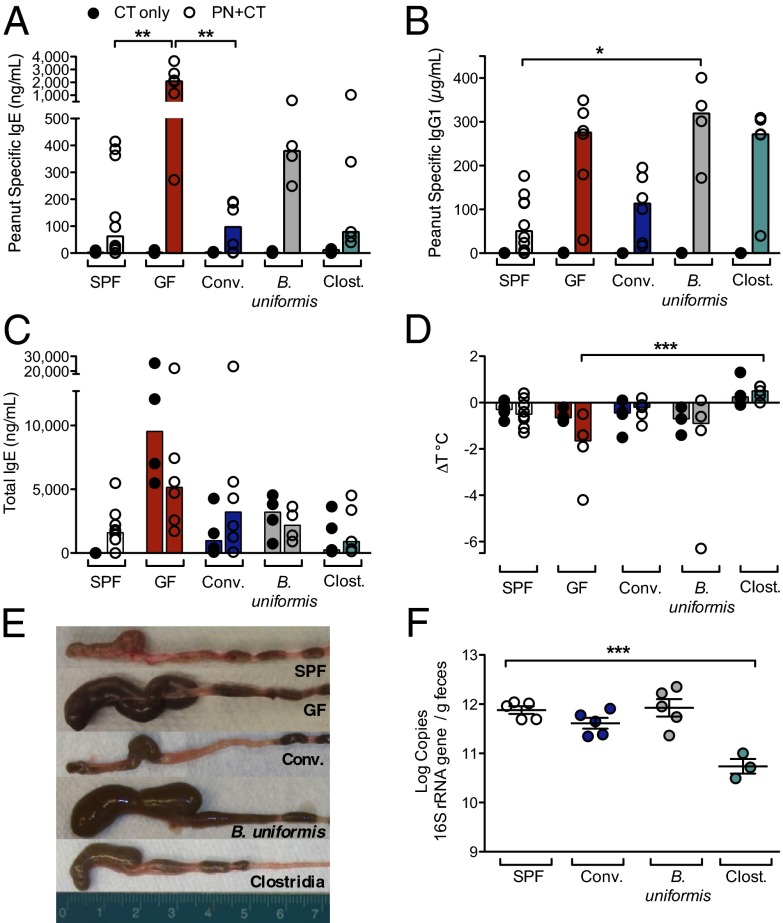
Fig. 2.
A Clostridia-containing microbiota protects against sensitization to food allergens. (A–D) Groups of SPF (white), GF (red), or gnotobiotic mice colonized with fecal/cecal material from SPF mice (Conventionalized, blue), B. uniformis (gray), or with a consortium of Clostridia (green) were sensitized with either CT only or PN/CT at weaning and challenged on day 35. (A) Concentration of PN-specific IgE, (B) IgG1, and (C) total IgE in serum of sensitized mice collected 24 h after challenge. (D) Change in core body temperature in sensitized mice (n = 4–10 mice per group from two independent experiments; closed circles, CT only; open circles, PN/CT). In A–D, each circle represents an individual mouse; bars depict median. (E) Cecal size at 13 d after colonization. (F) Bacterial load in feces collected from 5- to 10-wk-old SPF and gnotobiotic mice 14 d after colonization. n = 3–5 mice per group. F depicts mean and SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 determined by two-way ANOVA with the Kruskal-Wallis test (A–D) or one-way ANOVA with Tukey posttest (F).