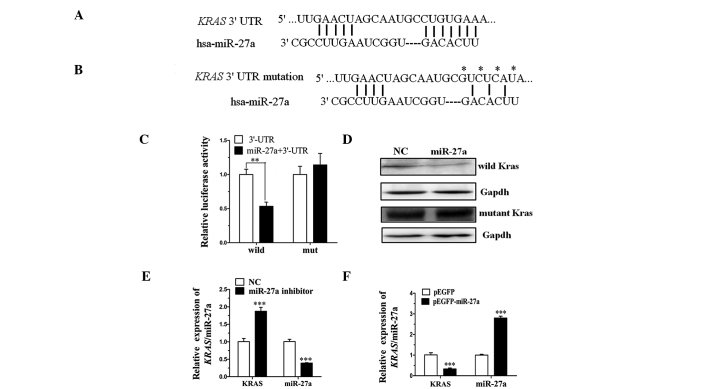
Figure 1.
miR-27a directly targets the KRAS gene by interacting with its 3′-UTR. (A) miR-27a binding sequence in the 3′-UTR of KRAS; and (B) a mutation of the KRAS 3′-UTR generated in the site complementary to the seed region of miR-27a. *Indicates the mutant nucleotide. (C) Relative luciferase activity (normalized control group activity) of HEK-293T cells tranfected with pGL3-Kras-3′-UTR or pGL3-Kras-3′-UTR/mut, and miRNA-NC or miR-27a mimics. (D) Western blot analysis indicating the expression of K-ras wild-type and mutant K-ras protein following miR-27a mimic or miRNA-NC transfection. GAPDH served as an internal control. (E and F) Relative expression of miR-27a and KRAS was detected by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction following miR-27a inhibitor or pEGFP-miR-27a transfection in TE-10 or TE-1 cells, respectively. *P<0.05 vs. NC transfected group; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. U6 small nuclear RNA and 18S RNA served as the internal controls in A and C, and B and D, respectively. Each assay was performed in triplicate. miRNA, microRNA; KRAS, Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; UTR, untranslated region; NC, negative control.