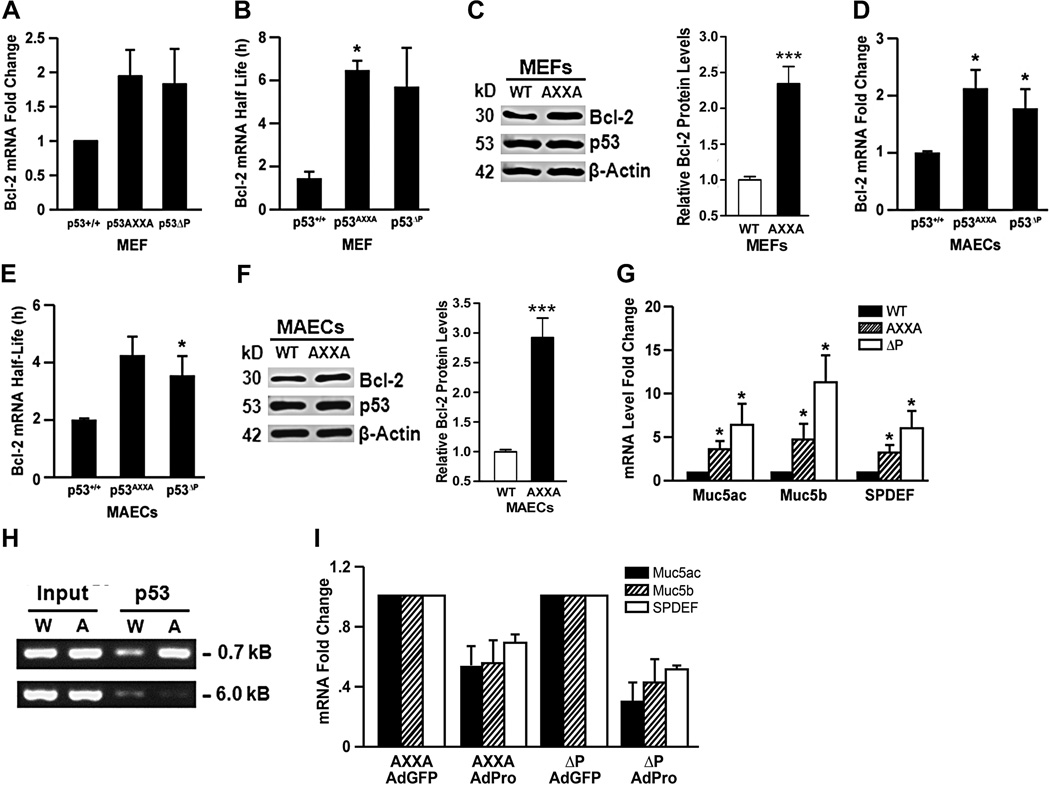
Figure 5. The proline-rich domain of murine p53 regulates bcl-2 mRNA levels and half-life, and the expression of mucous differentiation genes.
Bcl-2 mRNA levels (A, D) and mRNA half-life (B, E) in MEFs (A, B) and in MAECs (D, E), respectively from p53WT, p53ΔP, and p53AXXA mice after treatment with 10 mJ UV light was determined after treating with DRB and collecting RNA samples at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12h for analysis by qRT-PCR. Experiments were repeated at least 3 times with each experiment containing 3–4 independent repeats. Bcl-2 protein levels in MEFs (C) and MAECs (F) from p53WT and p53AXXA mice with densitometric quantification of Bcl-2 protein levels normalized to actin content shown in the lower panels. (G) MAECs isolated from p53WT, p53AXXA and p53ΔP/ΔP mice were differentiated on air-liquid interface cultures on Transwell membranes and RNA analyzed by qRT-PCR for Muc5ac, Muc5b, and SPDEF. (H) ChIP assay using p53 antibodies from p53WT and p53AXXA MEFs showed that significantly more DNA was pulled down from the AXXA cells compared to the WT cells. Input denotes that similar DNA amounts were used for the pull-down experiment. Interaction of p53 is visible when using primers specific to the −0.7 kB region but absent when using primers specific to the −6 kB region. (I) p53AXXA and p53ΔP MAECs were differentiated on air-liquid interface cultures and infected with adenoviruses AdGFP (control) and AdPro. Isolated RNA was analyzed by qRT-PCR for Muc5ac, Muc5b, and SPDEF. Bars = group means ± standard error from the mean (n = 3 different treatments/group); * P<0.05.