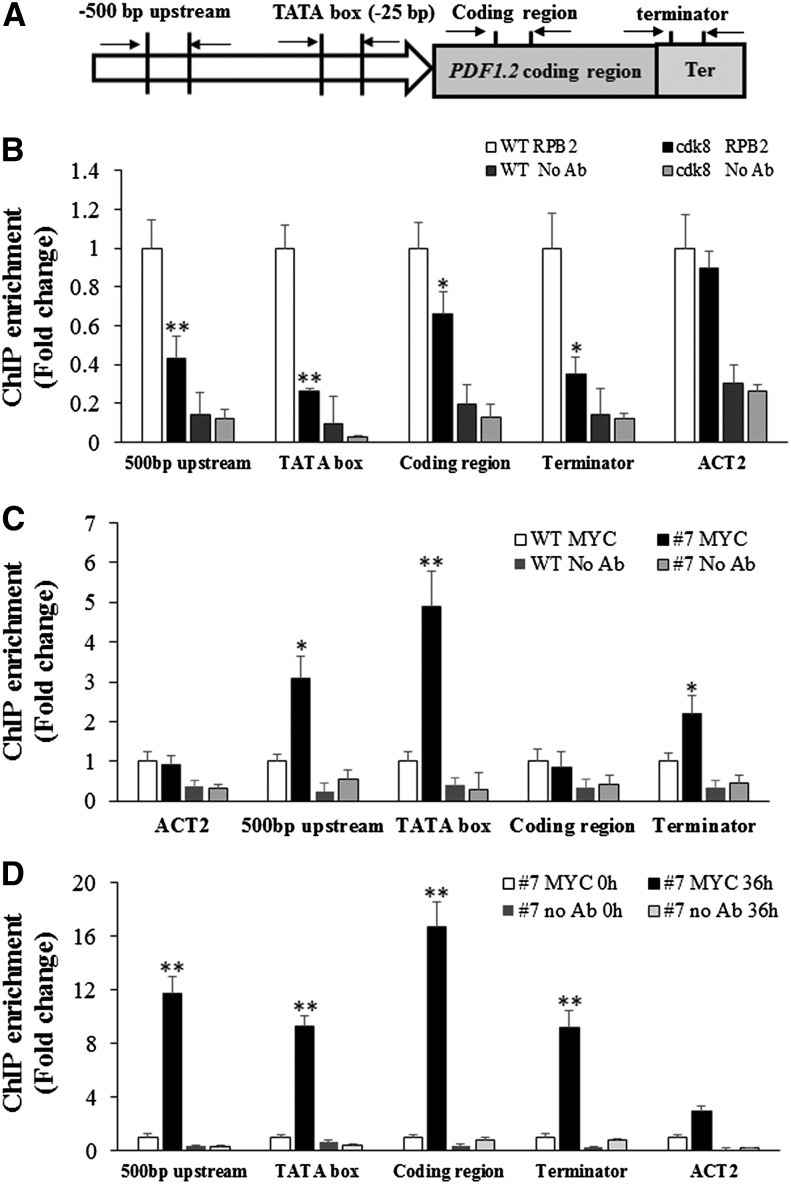
Figure 4.
CDK8 Associates with the Regulatory Regions of the PDF1.2 Gene.
(A) Schematic showing the positions of PDF1.2 gene primers used for ChIP-qPCR.
(B) CDK8 is required for MeJA-induced RNAP II recruitment to the PDF1.2 promoter. ChIP-qPCR results are shown with PDF1.2 gene-specific primers. Chromatin was extracted from wild-type and cdk8 seedlings 1 h after treatment with 100 μM MeJA and then precipitated with anti-RPB2 antibody (Abcam) or only IgG (negative control with no antibody [No Ab]). The RNAP II recruitment at Arabidopsis ACT2 was used as a control because its expression is independent of CDK8. The ChIP-qPCR data show that RNAP II recruitment to PDF1.2 500-bp, TATA box, and coding and terminator regions decreased compared with the wild type.
(C) CDK8 associates with the PDF1.2 promoter. Chromatin was extracted from 5-week-old wild-type and cdk8;35S:CDK8-MYC transgenic plants and then precipitated with anti-MYC antibody (Abcam) or only IgG (No Ab).
(D) Recruitment of CDK8 to the PDF1.2 promoter is significantly enhanced by B. cinerea infection. Chromatin was extracted from 5-week-old cdk8;35S:CDK8-MYC #7 transgenic plants that were mock-inoculated or B. cinerea spray-inoculated. ChIP was performed with anti-MYC antibody (Abcam) or only IgG (No Ab). The CDK8 recruitment to 500-bp upstream, TATA box, and coding and terminator regions of PDF1.2 was determined by quantitative PCR using primers at different positions of the PDF1.2 gene as shown in (A).
Error bars in (B) to (D) indicate se (n = 3). Two biological replicates were performed with similar results for each ChIP-qPCR experiment. The significance of differences in mean values is marked by asterisks (Student’s t test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).