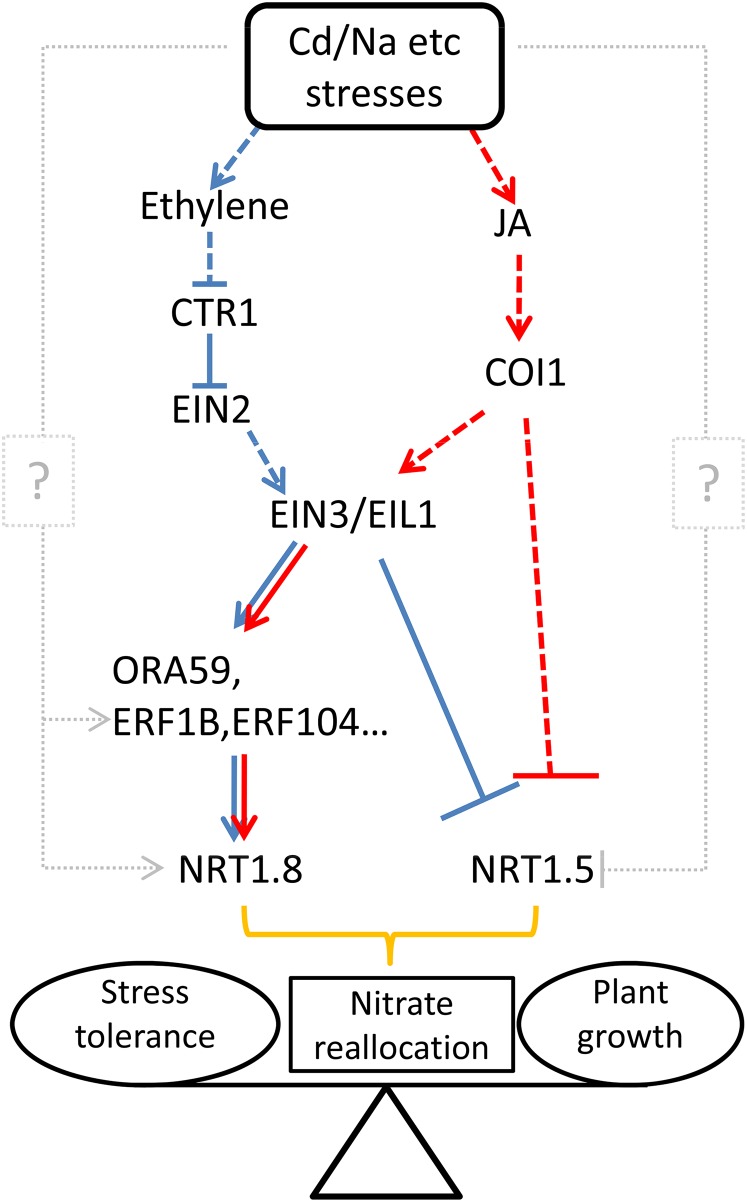
Figure 10.
A Simplified Model for the Interaction between ET/JA Signaling and Nitrate Reallocation to Mediate Plant Adaptation to the Environment.
Stresses such as cadmium or salt induce the production of ET and JA, which further activates the ET and JA signaling pathways, respectively. EIN3/EIL1 acts to converge signals transduced by ET and JA cascades, and further transduces the signal down to ERFs, which induce NRT1.8 expression by binding to its promoter, or EIN3/EIL1 decodes signals via the ET pathway by binding to the promoter of NRT1.5 and suppresses its expression. The JA pathway also participates in the downregulation of NRT1.5 via COI1. The coordinated upregulation of NRT1.8 and downregulation of NRT1.5 fine-tunes nitrate reallocation to roots, which modulates the balance between stress tolerance and plant growth. Blue lines display the route for signals going through the ET signaling pathway, while red lines indicate those through the JA signaling pathway. Dashed lines indicate steps not shown or possible unidentified components. Gray dotted lines and question marks indicate alternative pathways/components that contribute, but to a much lesser extent, in the regulation of NRT1.5 and NRT1.8.