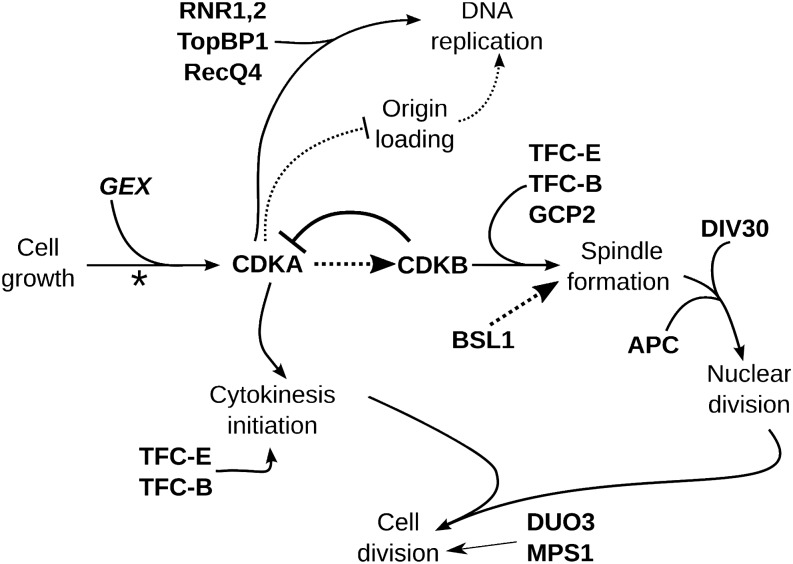
Figure 8.
Chlamydomonas Cell Cycle Regulation.
In natural conditions, small newborn cells probably hatch at dawn. Photosynthesis supports severalfold (2n-fold) cell growth in G1 during the day (dependent on the GEX genes) and division occurs at night. In mid-G1, the “commitment” point marks a decision to complete cell division (asterisk). Cell division consists of multiple cycles of DNA replication, nuclear division, and cytokinesis. We hypothesize that CDKA is a key initiator of the cell division program, promoting DNA replication and initial steps in cytokinesis. Mitotic progression is then primarily driven by CDKB. CDKA may activate CDKB; CDKB in turn is required to downregulate CDK activity at the end of mitosis. These ideas, and the placement of other genes in this regulatory scheme, are explained in the text.