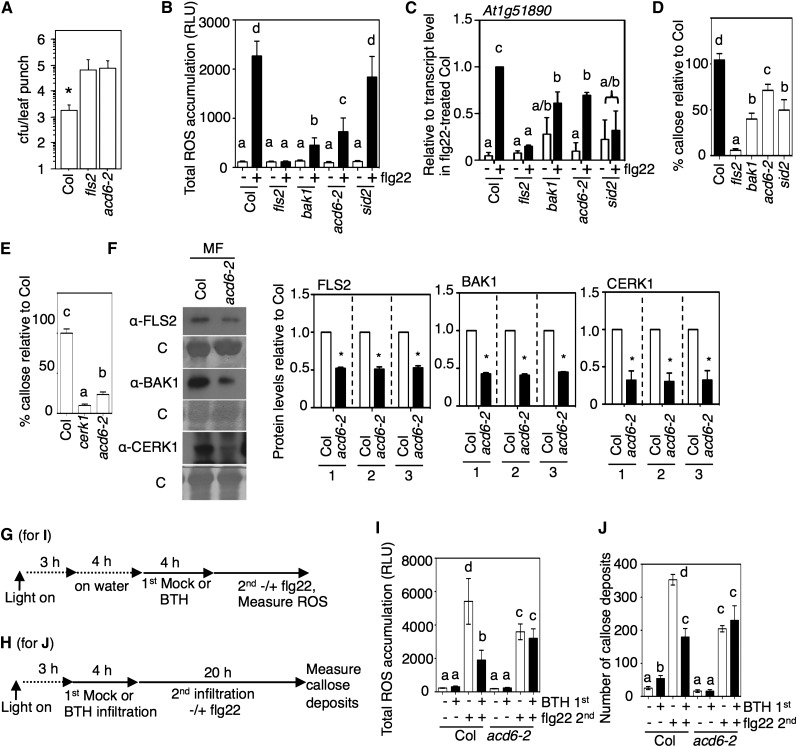
Figure 6.
The acd6 Null Mutant Shows Decreased Responses to flg22 and Reduced Receptor Levels.
(A) Increased colonization of type III secretion-deficient P. syringae in plants lacking ACD6. The acd6-2 mutant and the wild type (Col) were sprayed with P. syringae pv maculicola ES4326 hrcC− at a dose of OD600 = 0.03, and 3 d later, bacteria were enumerated from eight leaf discs per genotype. fls2 was included as a control for increased colonization. Colonization of mutant plants was higher than that seen in the wild type (*P < 0.04, t test). cfu, colony-forming units.
(B) to (D) Analysis of acd6-2 in comparison with fls2, bak1-4, and sid2-1. – or + indicates the absence or presence of flg22 in (B) and (C).
(B) Total ROS accumulation after 1 µM flg22 treatment (as in Figures 1A and 1E) in the indicated plants (n > 10). RLU, relative light units.
(C) Transcript levels of the flg22-induced gene At1g51890 in the indicated plants relative to wild-type (Col) plants 1 h after infiltration with 1 µM flg22 determined by qRT-PCR.
(D) and (E) Callose deposition 18 h after 1 µM flg22 (n = 8) (D) or 24 h after 10 µg/mL chitin (n > 24) (E) infiltration in leaves of the indicated plant lines as a percentage of callose in the wild type (Col).
(F) FLS2, BAK1, and CERK1 protein levels are low in the membrane microsomal fraction (MF) of acd6-2 relative to wild-type plants. Microsomal fraction proteins isolated from plants were analyzed by immunoblotting with FLS2, BAK1, and CERK1 antibodies. Graphs show the mean fold change in receptor levels (normalized to total protein [1], Rubisco only [2], or all proteins except Rubisco [3]) of acd6-2 relative to the wild type (Col) quantified using immunoblots using three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, which indicates that the acd6-2 values were different from wild-type values.
(G) and (H) Chemical treatment schemes for the indicated panels: (G) for (I); (H) for (J). In (G), “on water” indicates that tissue was excised and floated on water to facilitate BTH uptake.
(I) ROS accumulation after flg22 treatment of Col or acd6-2 leaves pretreated for 4 h with BTH or flg22 (n > 10).
(J) Callose deposition in leaves infiltrated with water (−), 1 µM flg22 (flg22 +), or 100 µM BTH (BTH +). Callose was detected 20 h after the second treatment in plants (n > 8).
Error bars in (A), (B), (D), (I), and (J) show sd from one representative experiment. Error bars in (C), (E), and (F) show se of three independent experiments analyzed together. Letters above bars represent significance groups as determined by the Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test, P < 0.05. These experiments were repeated three times with similar results.