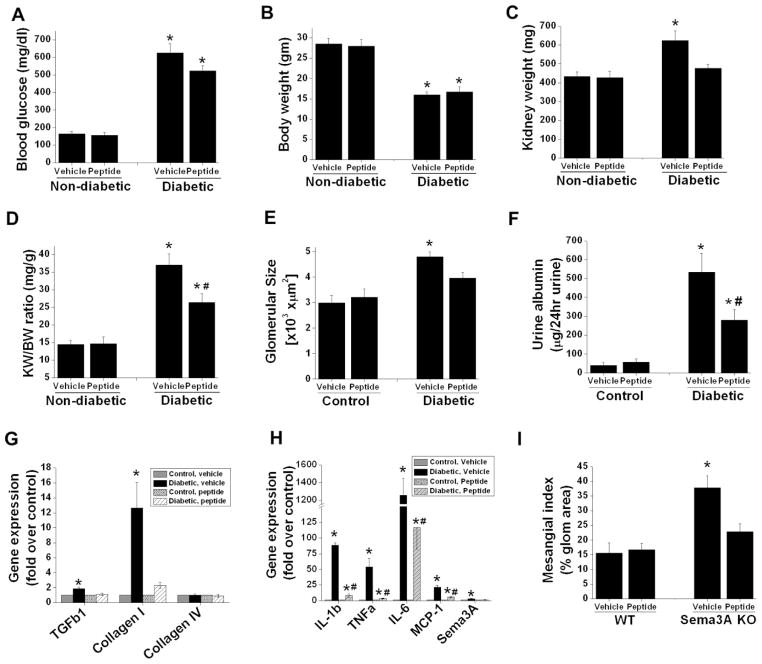
Figure 5.
Sema3A complimentary peptide administration suppressed diabetes induced albuminuria and inflammation. DBA/2J mice made diabetic by administering low dose of STZ as described in Methods. Non-diabetic animals received citrate buffer. 4 weeks after confirmation of diabetes animals received either 10μg/animal/day of scrambled peptide (vehicle) or sema3A complimentary inhibitory peptide (peptide) for another 6 weeks. Animal tissue and urine was processed for histopathology and albumin quantification. A. Blood glucose significantly elevated both in vehicle and peptide treated diabetic animals. *,p<0.001 vs. non-diabetic animals. B. Body weight significantly reduced in both vehicle treated and peptide treated diabetic mice. *, p<0.001 vs. non-diabetic mice. Administration of inhibitor peptide to sema3A significantly reduced diabetes induced kidney weight (C) and kidney weight/bodyweight ratio (D) suggesting that reduction of kidney hypertrophy with peptide treatment. *, p<0.05 vs. non-diabetic group. #, p<0.05 vs. vehicle treated diabetic group. E. Diabetes induced a significant increase in glomerular area in vehicle treated diabetic mice which was reduced with sema3A antagonist peptide treated diabetic mice. *, p<0.05 vs. all other groups. n=6–8. F. Albumin excretion rate expressed as μg/24hr urine. *, p<0.001 vs. other groups. G. Profibrotic gene expression is significantly increased in diabetic animals treated with vehicle as compared to control animals. Administration of peptide completely suppressed profibrotic gene expression. *, p<0.01 vs. other groups. H. Diabetes induced a large increase in inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression as compared control animals which was largely suppressed in peptide administered diabetic animal kidney. *, p<0.001 vs. other groups. #, p<0.05 vs. control. n=6–8. I. Diabetes induced a significant increase in mesangial matrix expansion in vehicle treated group as compared inhibitory peptide treated group. *, p<0.05 vs. other groups. n=6.