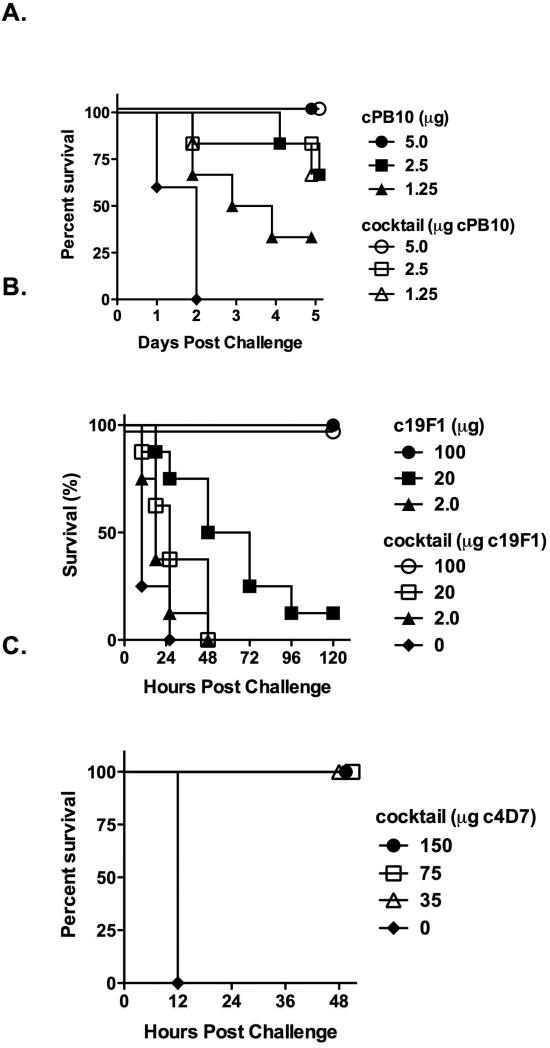
Figure 2. Protection afforded by the tripartite mAb cocktail in mice upon challenge with ricin, SEB and ETX.
The tripartite mAb cocktail was assessed for the ability to protect mice against ricin (panels A, D-F), SEB (panel B) and ETX (panel C). All studies involving mice were done in strict compliance the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees (IACUC) at the Wadsworth Center, Iowa State University, and University of California, Davis. (A) BALB/c mice (female, 6-8 weeks of age; Taconic Labs, Hudson, NY) were housed under conventional, specific pathogen-free conditions. cPB10, alone or in the cocktail was administered to mice (n=10/group) by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection 24 h prior to challenge with 10x LD50 ricin (~2 μg mouse; Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA), also by i.p. injection. Survival was monitored over a period of five days. (B) To evaluate c19F1, the chimeric mAb alone or in the context of the cocktail was mixed with SEB (1 μg) for 1 hr and then injected into BALB/c mice (Karauzum et al., 2012). Four hours later the animals received a potentiating dose of lipopolysaccharide (40 μg; List Biological Laboratories, Campbell, CA) and were monitored for survival for 5 days. (C) To evaluate c4D7, the chimeric mAb in the context of the cocktail was administered to female BALB/c mice by i.p. injection, as described previously (Garcia et al., 2014). Twenty-four hours later, the animals were challenged by intravenous injection 3xLD50 ETX.