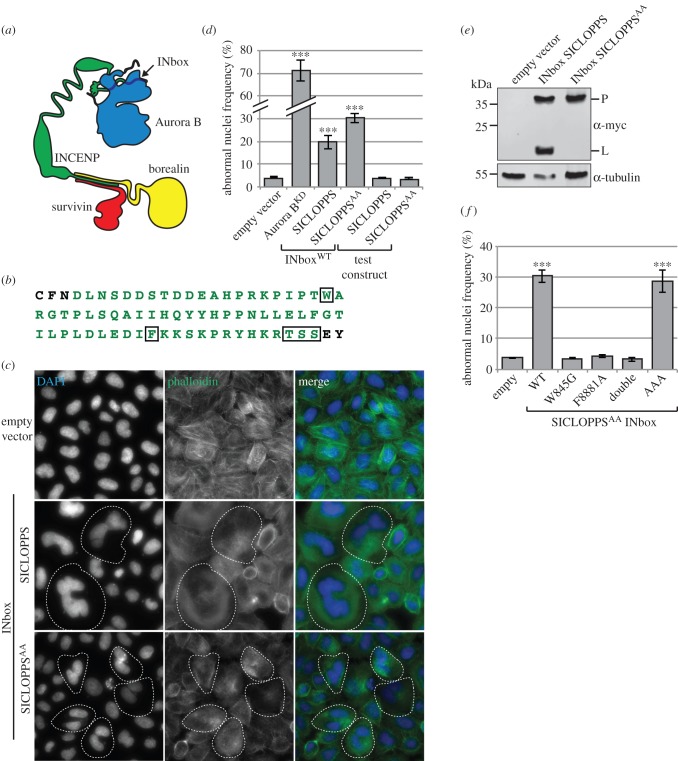
Figure 2.
Soluble IN-box expression impairs CPC function. (a) Representation of the CPC highlighting the location of the IN-box (adapted from [6]). (b) Sequence of the soluble IN-box fragment inserted into the SICLOPPS construct containing IN-box residues (green) flanked by native Ssp DnaE extein residues (black). Boxed regions indicate location of mutations made to yield IN-boxW845G, IN-boxF881A, IN-boxdbl and IN-boxAAA constructs. (c) Representative micrographs of DAPI and rhodamine phalloidin-stained puromycin-selected cells transiently expressing soluble IN-boxWT constructs for 48 h. Dotted outlines indicate cells with nuclear morphological aberrations. (d) Quantification of abnormal nuclei frequency (ANF) in the same samples as the previous panel as well as for an Aurora B kinase-dead control. (e) Quantitative western blot detection of the SICLOPPS linear precursor (P) and the faster migrating linear product (L) in samples treated as in (c). Unspecific bands are marked with an asterisk. (f) Quantification of the ANF elicited by SICLOPPSAA IN-box mutant constructs under identical conditions to those outlined in (c). (for (c) and (f): n = 3; more than 1000 cells per replicate; error bars: ±s.e.m.; *** indicates a significance of p < 0.001 between the sample and empty vector control as determined using the χ²-test).