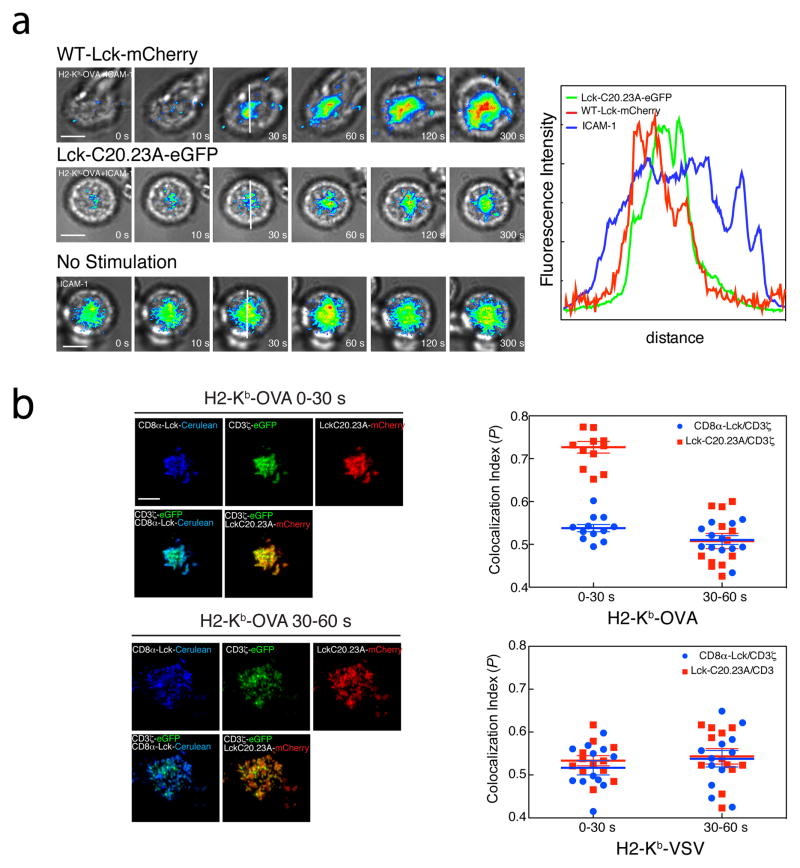
Figure 8. Lck recruitment analysis.
(a) OT-I Rag1−/− CTL were transduced with wild-type mCherry fused Lck (top row) or mutant LckC20.23A-eGFP (middle row), added to lipid bilayers containing H2-Kb-OVA monomers and ICAM-1(top two rows), or ICAM-1 only (bottom row), and the immune synapses were imaged under TIRF microscopy. Cells can be followed by transmitted light. Lck intensity is shown in false color at selected time points. Scale bar 5 μm. Bottom, intensity line profile of cell interacting with bilayers containing H2-Kb-OVA monomers and ICAM-1 (green) or ICAM-1 only (blue). Data are representative of three experiments. (b) Double colocalization analysis of immune synapses from OT-I.ZG.8αLckC.8β.Lck C2023A.R cells interacting with lipid bilayers containing H2-Kb-OVA (left) or H2-Kb-VSV(right) plus ICAM-1. Scale bar 5 μm. Means ± s.e.m. of two separate experiments of Pearson′s coefficient between CD3ζ-eGFP and Lck-C20.23A-mCherry (red squares) or CD3ζ-eGFP and CD8α-Lck-Cerulean (blue circles) were plotted.