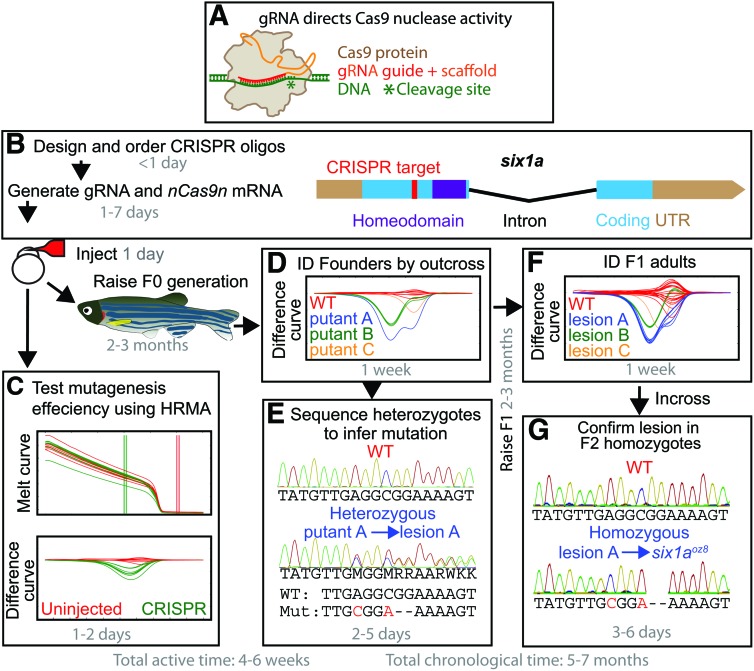
FIG. 1.
Mutagenesis pipeline with time estimates. (A) Illustration of a Cas9-gRNA complex bound to target DNA.12 (B) Example of CRISPR target site design for six1a (NCBI Gene ID 494168), with the target sequence downstream of potential alternative start sites and upstream of the homeodomain. (C) Polymerase chain reaction products from a subset of injected embryos (green lines) are subjected to a high-resolution melt curve and normalized to uninjected curves (red lines), revealing the melting difference caused by injection. (D) High-resolution melt analysis (HRMA) difference curves identifying three potentially different lesions in six1a were (E) sequenced from heterozygous F1 generation embryos. HRMA curves identified in this initial analysis are confirmed by (F) genotyping adult F1 generation fish fin DNA. (G) Homozygous mutant F2 generation sequence reads confirm the lesions inferred from heterozygous F1 generation sequences. Once confirmed, lesions are given allele designations. The mutation in six1a lesion A is six1aoz8, a 2 bp deletion that frameshifts Six1a after amino acid 93 of 284 and introduces 37 aberrant aa before terminating. Sequence analysis for lesion B (six1aoz9), which frameshifts Six1a after amino acid 94 and introduces only 12 aberrant aa, is described in the Supplementary Data. Lesion C is another 2 bp deletion (not shown). Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/zeb