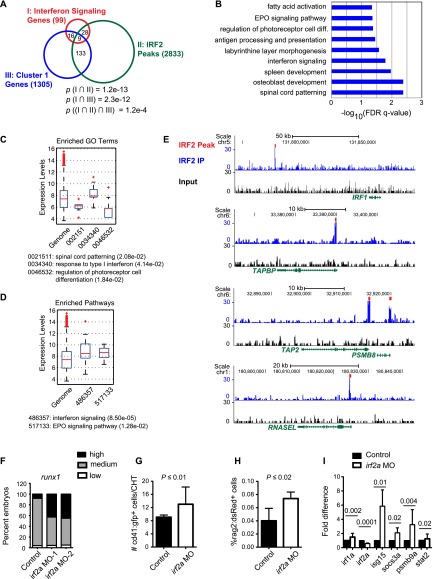
Figure 6.
IRF2 target genes in human CD34+ FL HSPCs overlap with IFN pathway genes and C1 genes. (A) Venn diagram of IFN signaling genes expressed in hCD34+ FL HSPCs, C1 genes (expressed in Ly6a-GFP+ HCCs), and IRF2-bound genes in hCD34+ FL HSPCs. P-values for overlap between all three sets were computed using a hypergeometric test. P-values for overlap of IRF2-bound and expressed genes were computed using GREAT. (B) Enriched GO biological process terms for IRF2-bound genes determined by GREAT. (C) Expression levels of IRF2-bound targets relative to all genes in hCD34+ FL HSPCs enriched for GO terms. P-values (in parentheses) as computed by t-test. Gene expression was analyzed from previously published Affymetrix microarray data (Xu et al. 2012). Only genes annotated with GO terms that had significantly different expression compared with the genome background are shown. (D) Expression levels of all genes and IRF2-bound genes in hCD34+ FL HSPCs enriched for representative pathway terms, as in C. (E) ChIP-seq signals for representative IFN pathway genes bound by IRF2. (F) Phenotype distribution of runx1 expression by WISH (AGM region) for irf2a morphants generated with two independent MOs compared with sibling controls (n ≥ 40 embryos per condition). (G) Absolute number of cd41:gfp+ HSPCs in the CHT of irf2a morphants at 38 hpf (n = 17; mean ± SD; t-test). (H) Percent of rag2:dsRed+ cells in whole embryos at 5 dpf by flow cytometry in irf2a morphants (n = 7; mean ± SD; t-test). (I) qPCR for IRF2 target genes in irf2a morphants (n = 2, from four replicates; mean ± SD; t-test).