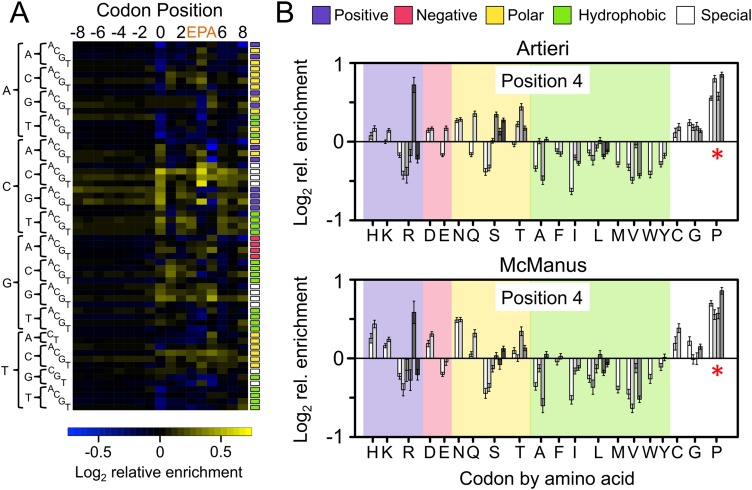
Figure 4.
The corrected Ribo coverage reveals a strong enrichment of proline codons. (A) Heatmap of the mean-scaled log2 enrichment of codon positions −8 to 8 in the Artieri data (the McManus data are similar) (Supplemental Fig. S9). All 61 sense codons are shown in alphabetical order indicated by their sequences on the left. Enriched codons are indicated by an increasing intensity of yellow color, while depleted codons are blue. Colored boxes to the right of each row indicate the biochemical category to which the codon belongs (color key is at the top of panel B). Codons associated with the E, P, and A active sites of the ribosome (positions 3, 4, and 5, respectively) are indicated. (B) Bar plots indicating the log2 enrichment values at position 4 of both the Artieri and McManus data sets. Codons are organized by amino acid using single-letter designations below the panel and grouped by biochemical type as indicated at the top of the panel. Individual codons for each amino acid are in alphabetical order. The 95% confidence intervals around the scaled enrichment values are indicated at the top of each bar. The asterisks indicate that proline (P) codons are more enriched than any other amino acid (Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test, P < 10−15).