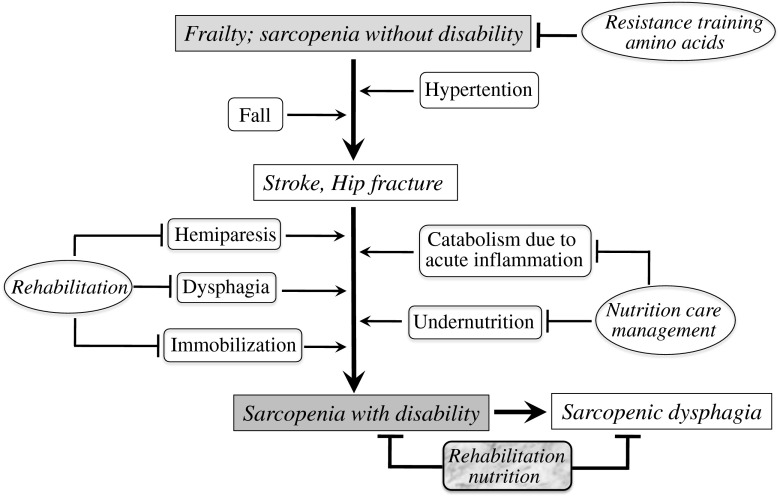
Fig. 1.
Mechanism of sarcopenia with disability in frail elderly with stroke and hip fracture. Frail elderly with stroke or hip fracture becomes sarcopenia with disability because of hemiparesis, dysphagia, immobilization, catabolism due to acute inflammation, and undernutrition. Rehabilitation for hemiparesis, dysphagia, immobilization, and nutrition care management for catabolism due to acute inflammation and undernutrition are usually provided separately. Sarcopenia with disability induces sarcopenic dysphagia which is characterized by the loss of swallowing muscle mass and function associated with generalized loss of skeletal muscle mass and function. Rehabilitation nutrition can be used to improve functionality in people with sarcopenic dysphagia and sarcopenia with disability