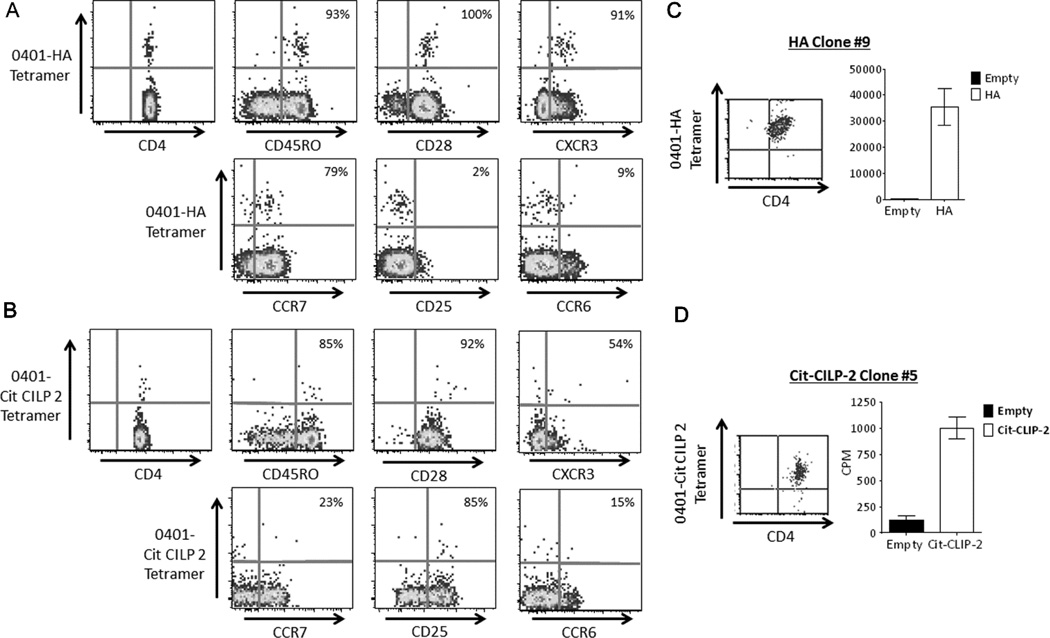
Fig. 2.
Flu and citrulline-specific CD4 T cells can reliably be detected ex vivo from the peripheral blood of RA patients. A) A representative example of ex vivo tetramer analysis for flu specific T cells from PBMC of an RA subject with a DR0401 haplotype after staining with DR0401-HA306–318 tetramer along with CD4, CXCR3, CD45RO, CD28, CCR7, CD25, and CCR6 antibodies. B) A representative example of ex vivo tetramer analysis for citrulline specific T cells from PBMC of an RA subject with a DR0401 haplotype after staining with DR0401-Cit-CILP 2 tetramer, CD4, CXCR3, CD45RO, CD28, CCR7, CD25, and CCR6 antibodies. C) DR0401- HA306–318 tetramer staining (left panel) and peptide specific proliferation (right panel) as seen by monomer stimulation (black bars=DR0401-empty monomer, white bars=DR0401-HA306–318 monomer) of a direct ex vivo sorted HA-T cell clone isolated from an RA patient. D) DR0401-Cit-CILP 2 tetramer staining (left panel) and peptide specific proliferation (right panel) as seen by monomer stimulation (black bars=DR0401-empty monomer, white bars=DR0401- Cit-CILP 2 monomer) of a direct ex vivo sorted Cit-CILP 2-T cell clone isolated from an RA patient.