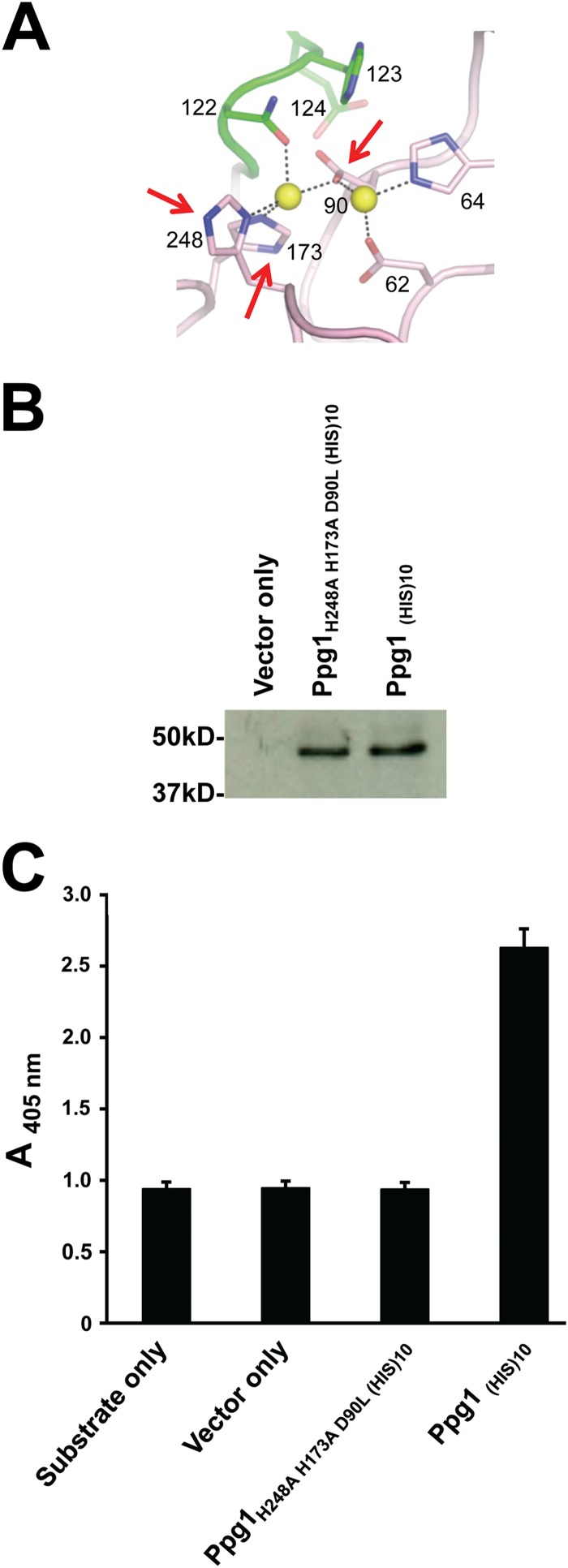
FIG 1.
Mutation of the putative Ppg1 catalytic site abolishes phosphatase activity. (A) A model for the putative Ppg1 catalytically active binuclear center generated using homology detection and structure prediction HMM-HMM comparison (HHpred) software (http://toolkit.tuebingen.mpg.de/hhpred). Numbered amino acids represent highly conserved residues in the putative catalytic site. Arrows indicate mutated residues. (B) His-tagged WT and mutated Ppg1 were expressed in an E. coli Rosetta 2(DE3) strain and purified from the supernatant of bacterial extracts using Ni-NTA agarose (Qiagen) affinity chromatography. Western analysis was performed using 20 μg of recombinant purified proteins and an anti-His primary antibody and goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody. (C) Phosphatase activity was determined using 20 μg of the indicated proteins and p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP) as a substrate.