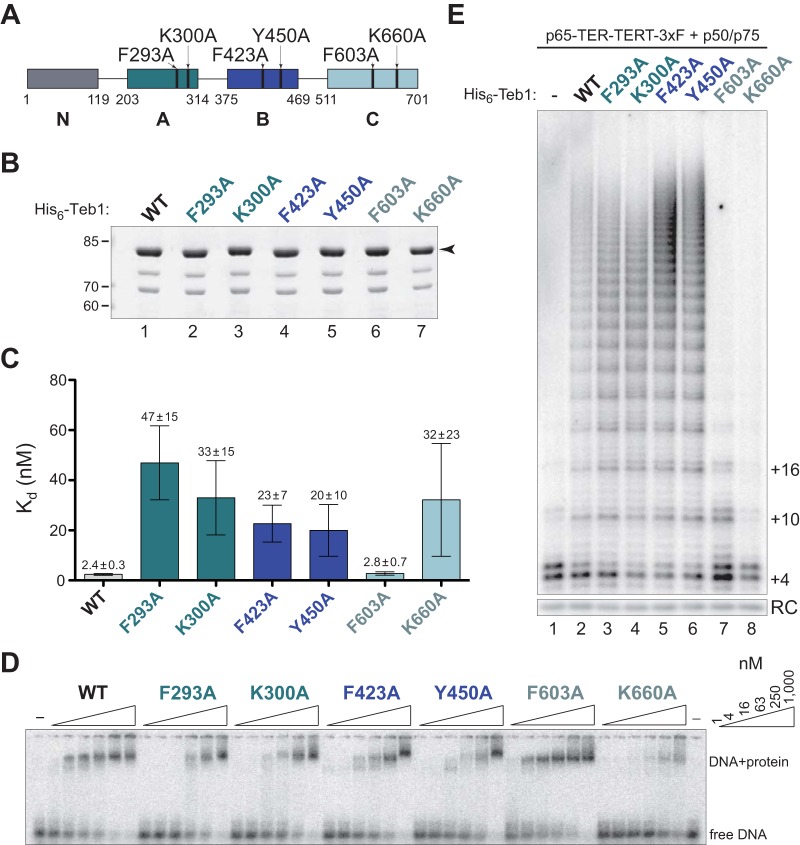
FIG 3.
Substitutions in canonical DNA binding surfaces of the A, B, and C domains of full-length Teb1 alter DNA binding or telomerase activity in vitro. (A) Schematic of full-length Teb1 single-residue substitutions used in this study. (B) SDS-PAGE of bacterially expressed and purified His6-Teb1 proteins. The arrowhead to the right of the gel indicates full-length Teb1; minor amounts of ∼75- and ∼65-kDa proteins are a copurifying contaminant and Teb1 truncated by proteolysis of the linker between the Teb1 B and C domains, respectively. (C and D) Calculated Kd for each of the Teb1 proteins as determined by EMSA in triplicate (C), with a representative EMSA (D). (E) Activity assay of recombinant full-length Teb1 reconstitution of holoenzyme catalytic activity.