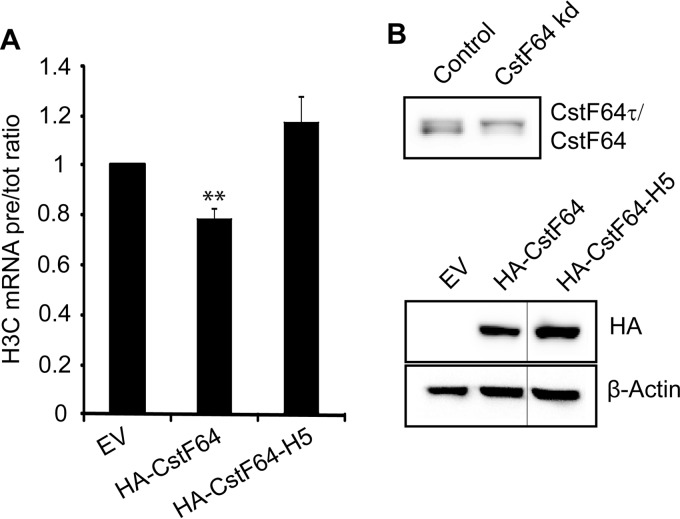
FIG 3.
Exogenous HA-CstF64 needs to interact with symplekin to complement a histone RNA processing defect caused by CstF64 depletion. CstF64-depleted cells (after 4 days of doxycycline induction) were transiently transfected with HA-tagged cDNAs for either wild-type CstF64 (HA-CstF64) or a CstF64 mutant unable to interact with symplekin (HA-CstF64-H5) (20) or with an empty vector (EV) as a control. Total RNA was isolated 24 h after transfection, and histone H3C precursor (pre-RNA) and total mRNA levels were quantitated by RT-qPCR. (A) H3C pre-RNA/total RNA ratios. HA-CstF64 reduces the precursor accumulation by ∼20% (P = 0.0089, Welch t test). In contrast, the mutant HA-CstF64-H5, unable to bind symplekin, fails to rescue the defect or even aggravates it (P = 0.0962). The error bars represent standard deviations from three biological replicates. (B) Western blots showing the efficiency of CstF64 depletion before transfection (upper panel) and the expression of tagged wild-type and mutant forms of CstF64 24 h posttransfection (lower panel). β-Actin was probed as a loading control. Thin vertical lines indicate where a lane has been omitted from the figure.