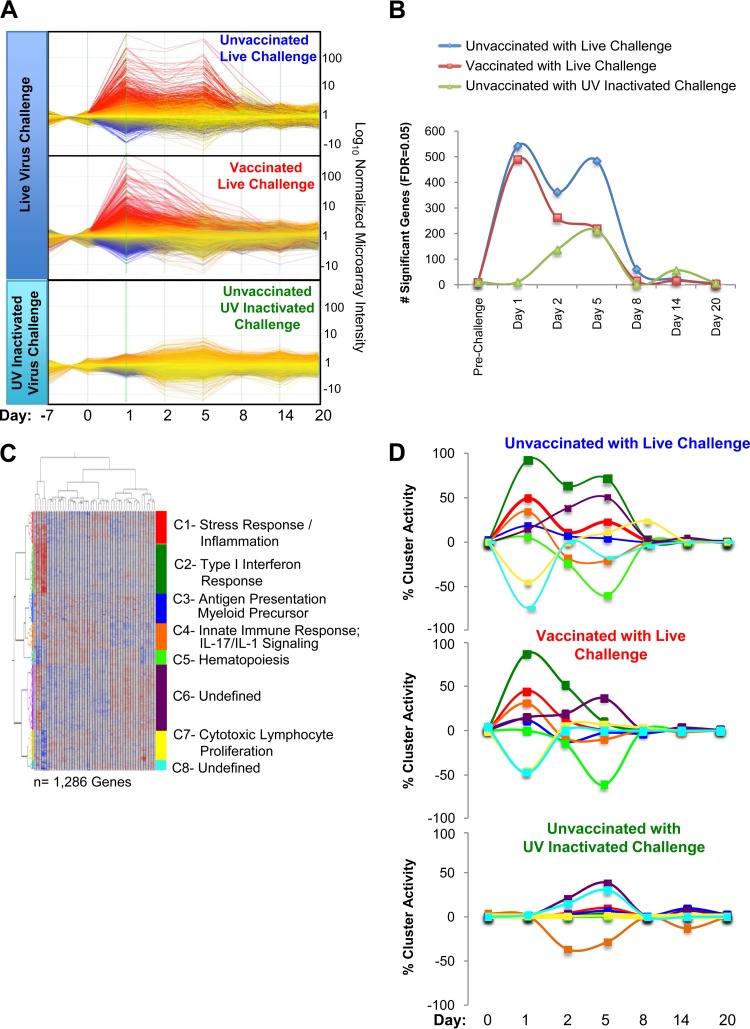
FIG 2.
Whole blood transcriptional profiling reveals signatures associated with viral challenge. (A) Transcriptional activity of all expressed genes normalized to prechallenge baselines reveals global changes in transcriptional signatures that differentiate animals challenged with live pH1N1 virus and those challenged with UV-inactivated virus. Furthermore, animals previously vaccinated with anti-LOX-1-HA and anti-DCIR-NP fusion proteins exhibited reduced transcriptional perturbations, especially on day 5 after challenge with live virus. Linear mixed models were employed to identify genes with differential abundance for each of the three animal groups relative to their respective preinfection baselines. (B) Number of genes with significant changes in abundance were plotted at each time point for each group. (C) The genes in panel B were then hierarchically clustered, and k-means (k = 8) were used to group genes with similar expression profiles across the time points. GeneGo pathway analysis was employed to annotate each cluster (Table 1; also see Table S1 in the supplemental material). (D) Percent cluster activity was calculated at each time point by determining the ratio of significant genes to the total number of genes constituting the cluster. The sign of the LMMA statistical estimate was used to assign positive or negative cluster activity relative to the preinfection baseline. Color coding for each cluster matches that presented in the heat map in panel C.