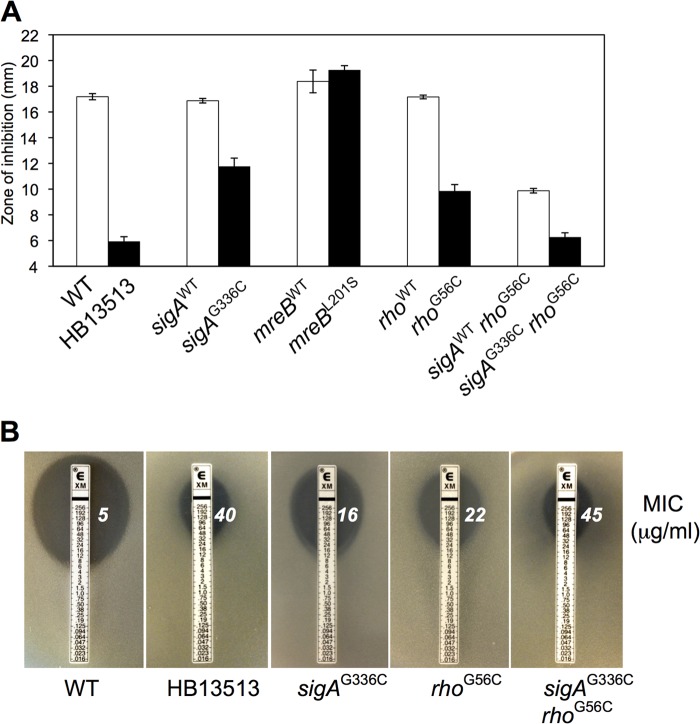
FIG 3.
Identification of the genetic determinants for decreased CEF susceptibility. (A) Determination of the CEF susceptibilities of the reconstructed strains. Note that in the course of introducing each of these mutations into the parent strain (by selection for the linked antibiotic resistance marker [Fig. 2A]), recombination can occur either proximal to the SNP (leaving a wild-type allele in the chromosome) or distal to the SNP (leading to a strain with the SNP in the chromosome). The former integrants, which provide a control to rule out effects from the integrated antibiotic cassette, are designated by a superscript WT, and the latter are identified by the corresponding amino acid change. Disk diffusion assays were performed on MH agar plates with a filter paper disk containing 50 μg CEF. Each bar represents the average zone of inhibition, expressed as the total diameter minus the diameter of the filter paper disk (6.5 mm). Three independent experiments were performed for each strain, and the standard deviations are indicated by error bars. (B) Determination of MICs for CEF using an Etest assay. The Etest strips (bioMérieux) with CEF concentrations of 0.016 to 256 μg/ml were applied to MH agar plates, and the MIC was read by interpolation after 18 h of incubation at 37°C.