FIG 3.
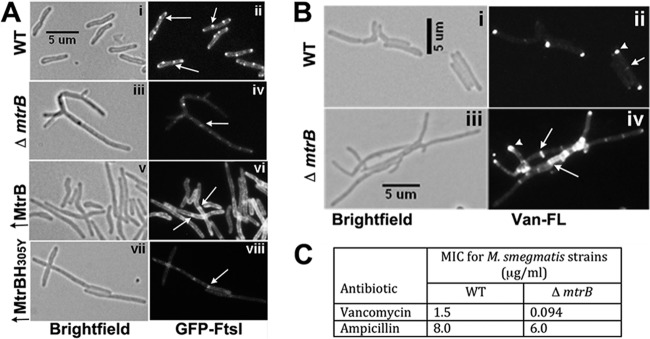
FtsI localization and activity are altered in the absence of MtrB. (A) GFP-FtsI localization was examined in M. smegmatis WT (i and ii), the ΔmtrB strain (iii and iv), and merodiploid strains overproducing (↑) MtrB (v and vi) or MtrBH305Y (vii and viii). In all of the strains, the GFP-FtsI fusion protein was produced from Pami::gfp-ftsI following induction with 0.2% acetamide for 3 h, visualized by bright-field (left panels) and fluorescent (right panels) microscopy, and imaged as described in the text. (B) The exponential cultures of the M. smegmatis WT strain (i and ii) and the ΔmtrB strain (iii and iv) were grown in the presence of Van-FL for 2 h and were imaged by bright-field (i and iii) and fluorescence (ii and iv) microscopy. (C) Loss of MtrB increases sensitivity to vancomycin. M. smegmatis WT and ΔmtrB strains were grown for 6 h, and 1 × 105 cells were spread on 7H10 agar plates. Etest antibiotic strips (ampicillin or vancomycin) were placed on the agar plates, plates were incubated for 4 days at 37°C, and MICs were measured as per the supplier's protocol.
