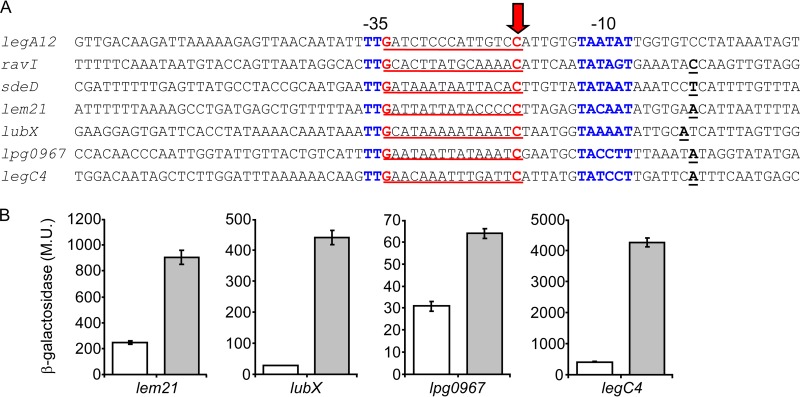
FIG 7.
Fis regulatory elements identified using a bioinformatics search. (A) The regulatory regions that were found to contain a putative Fis site which overlaps the −35 promoter element of the effector-encoding genes are presented. The nucleotides representing the putative Fis consensus are in red and underlined, the transcription start sites are in bold and underlined, the −10 and −35 promoter elements are in blue, and the C nucleotides that were mutated are marked with an arrow. The effector designations are indicated on the left. (B) Mutations constructed in the putative Fis regulatory elements resulted in elevated levels of expression at exponential phase. The expression levels of effector (indicated below the bars) wild-type lacZ fusions (white bars) and lacZ fusions of the same genes containing a mutation in a putative Fis binding site (gray bars) were examined at the exponential phase in the L. pneumophila wild-type strain. The mutations constructed are marked with a red arrow in panel A. β-Galactosidase activity was measured as described in Materials and Methods. Data (expressed in Miller units [M.U.]) are the averages ± standard deviations (error bars) of the results of at least three different experiments.