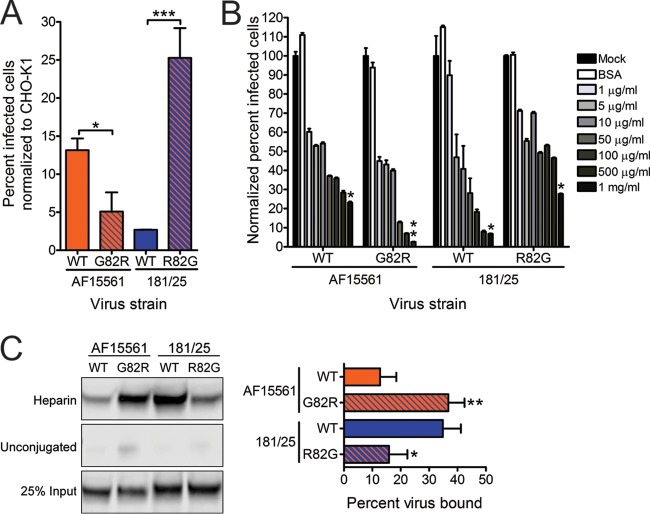
FIG 4.
An arginine at E2 residue 82 confers greater dependence on glycosaminoglycans. (A) CHO-K1 and CHO-pgsA745 cells were adsorbed with virus strain AF15561, 181/25, AF1561 E2 G82R, or 181/25 E2 R82G at an MOI of 10 PFU/cell and incubated for 24 h. Wild-type (WT) CHIKV or variant strains containing substitutions at E2 residue 82 were tested. The cells were stained with CHIKV-specific antiserum and DAPI to detect nuclei and imaged by fluorescence microscopy. Results are presented as percent infected cells for triplicate experiments normalized to the values for parental CHO-K1 cells. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means. (B) Strains AF15561, 181/25, AF1561 E2 G82R, and 181/25 E2 R82G were treated with BSA at 1,000 μg/ml or heparin at the concentrations shown for 30 min and adsorbed to Vero cells at an MOI of 2.5 PFU/cell. After incubation for 24 h, cells were stained with CHIKV-specific antiserum and DAPI to detect nuclei and imaged by fluorescence microscopy. Results are presented as percent infected cells for triplicate experiments normalized to the values for mock-treated virus. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means. (C) The virus strains shown at 5 × 109 genome copies each were incubated with heparin-conjugated or unconjugated agarose beads for 30 min, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and detected by immunoblotting with CHIKV E2-specific MAb (left). Twenty-five percent of input virus is shown as a control. The percentage of virus bound to beads was quantified by optical densitometry for triplicate experiments (right). Error bars indicate standard deviations. Values that are significantly different, as determined by Student's t test (A and C) and Kruskal-Wallis analysis followed by Dunn's posthoc test (B), are indicated by asterisks as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.