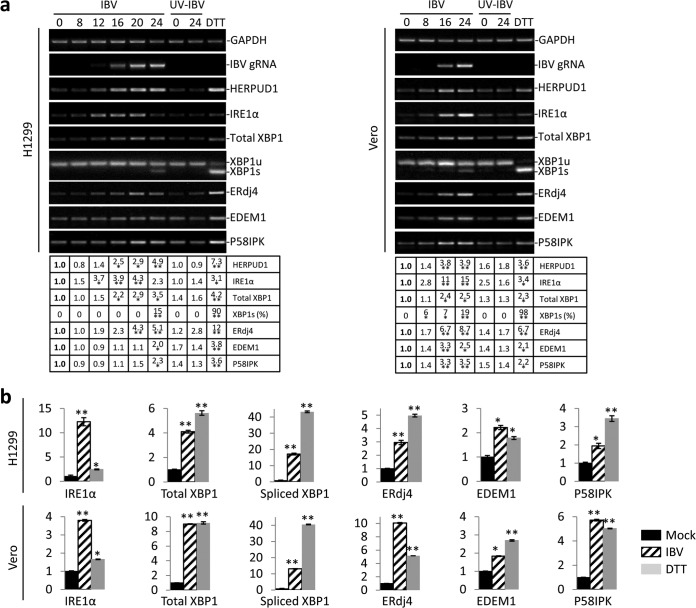
FIG 1.
Activation of the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway by IBV infection. (a) IBV infection causes ER stress and partially activates the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway in H1299 cells and Vero cells. H1299 cells (left) or Vero cells (right) were infected with IBV (MOI, ∼2) or incubated with UV-IBV and harvested at the time points indicated at the top (hours). As a positive control, H1299 cells were treated with 2 mM DTT for 2 h. Total RNA was extracted and subjected to RT-PCR using primer pairs specific for the indicated genes. The PCR products were resolved using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, except for XBP1u/XBP1s, where a 4% agarose gel was used. The band intensities of HERPUD1, IRE1α, total XBP1, EDEM1, and ERdj4 were determined by densitometry and normalized to the intensities of the corresponding GAPDH bands. The percentage of XBP1 splicing [XBP1s (%)] was calculated as the intensity of XBP1s divided by the total intensities of XBP1u and XBP1s. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results, and the result of one representative experiment is shown. The asterisks indicate significant differences between the indicated samples and the 0-h p.i. sample (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01). (b) H1299 cells and Vero cells were infected with IBV, mock infected for 20 h, or treated with DTT as for panel a. Total RNA was extracted and subjected to real-time RT-PCR analysis. The fold inductions of specific genes were calculated using GAPDH as an internal reference and normalized to the mock-infected samples. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results, and the result of one representative experiment is shown. The asterisks indicate significant differences between the indicated samples and the mock-treated sample (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01). The error bars indicate standard deviations.