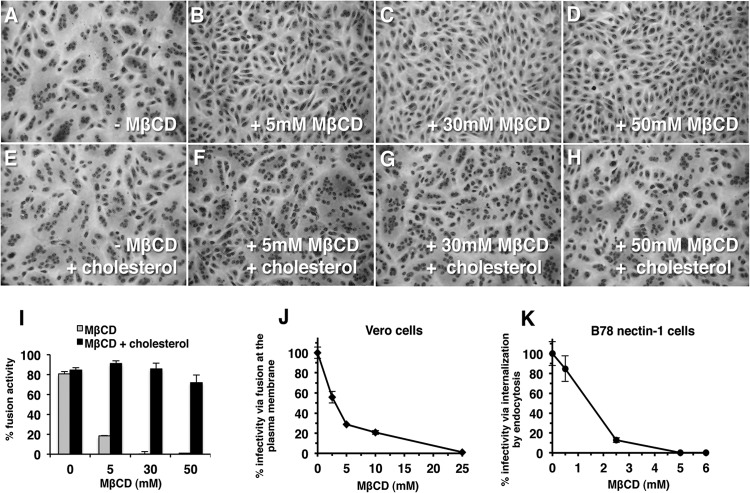
FIG 1.
Role of plasma membrane cholesterol in virion-induced fusion. Vero cells were mock treated (A, E) or treated with 5 mM (B, F), 30 mM (C, G), or 50 mM MβCD (D, H) for 30 min at room temperature. Cells were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and were then either mock treated (A to D) or treated with 200 μg/ml water-soluble cholesterol (E to H) for 30 min at 37°C. Then, cells were washed twice with PBS, and HSV-1 strain ANG path (MOI of 100) was added for 3 h at 37°C in the presence of 0.5 mM cycloheximide (Sigma) (A to H). Cells were fixed with 100% methanol and stained with Giemsa (Sigma). Magnification, ×20. (I) Fusion activity is defined as a/b × 100, where a = the number of nuclei sharing a cytoplasm with at least two other nuclei and b = total nuclei. More than 500 nuclei were evaluated per experimental condition. Each drug treatment was tested in triplicate in at least two independent experiments. (J, K) Vero (J) or B78-nectin-1 cells (K) in 24-well culture dishes were treated with MβCD for 30 min at room temperature. Cells were rinsed with PBS and then with complete Dulbecco modified Eagle medium. HSV-1 strain KOS (100 PFU) was added for 1 h at 37°C to allow viral entry. Cells were treated with sodium citrate (pH 3) to inactivate virus that remained at the plasma membrane. At 18 h p.i., cultures were fixed and plaque formation was determined by immunoperoxidase staining with anti-HSV polyclonal antibody HR50 (Fitzgerald Industries, Concord, MA). Data are mean results of duplicate determinations. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments.