FIG 4.
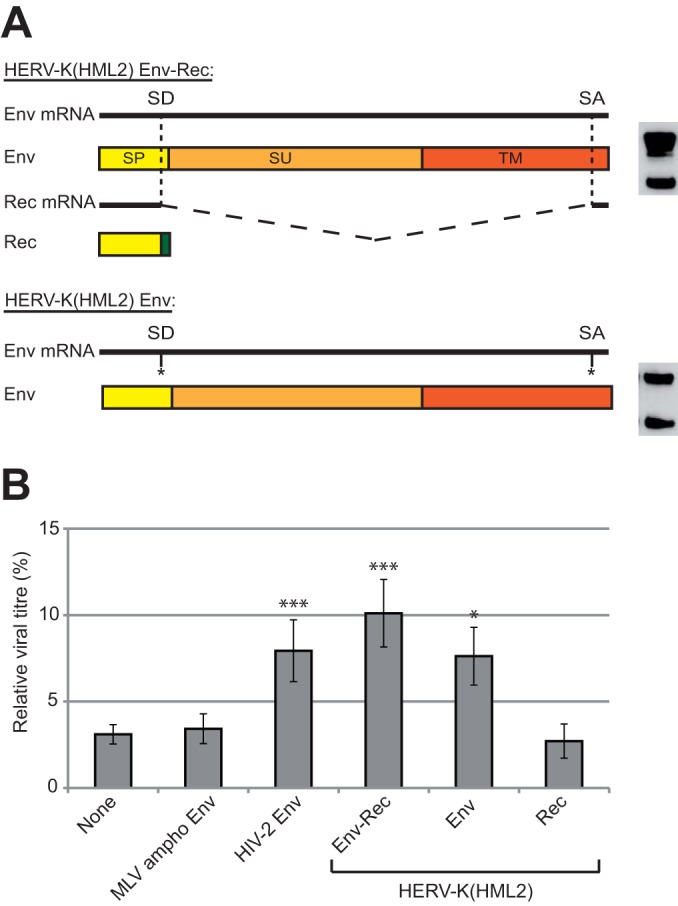
HERV-K(HML2) Env inhibits Tetherin activity. (A) The HERV-K(HML2) Env-Rec plasmid leads to the expression of 2 distinct proteins via alternative splicing: the full-length RNA encodes Env, a glycoprotein that is cleaved into 2 subunits during synthesis (surface subunit, SU, and transmembrane subunit, TM), while internal splicing sites (SD for splice donor and SA for splice acceptor) lead to the production of Rec, an accessory protein whose first exon (in yellow) is contained within the signal peptide (SP) of Env while the second exon (in green) is translated from a different reading frame. An expression vector leading to the production of Env but not Rec was generated by point mutations introduced in the splicing sites. Env expression levels obtained with each of the two constructs are shown on the right. (B) The ability of HERV-K(HML2) Env and Rec to antagonize Tetherin restriction was assayed as described in the legend to Fig. 2A. Results are given as described in the legend to Fig. 3A.
