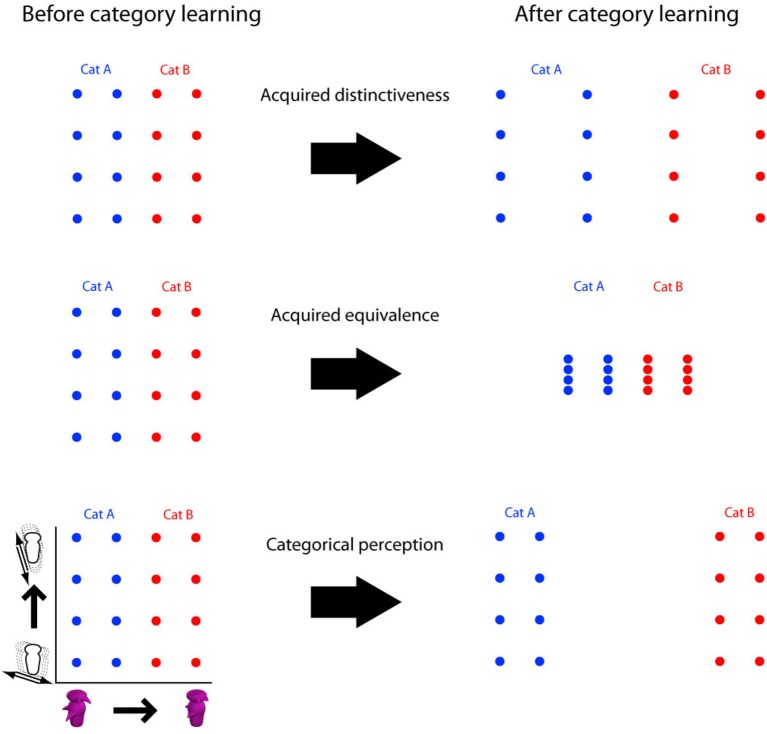
Figure 1.
Three types of dimensional modulation as a consequence of category learning. Dots represent positions of stimuli within a 2-dimensional space of objects. Changes in discriminability are represented by stretching and shrinking of the space. Acquired distinctiveness: a global increase in discriminability along the category relevant dimension. Acquired equivalence: a decrease in discriminability along the irrelevant dimension. Categorical perception: an increase in discriminability local to the region around the category boundary.